How To Machine Aircraft Titanium: Plunge And Sweep For Finishing Corners
Part of a series of articles on more efficient machining of pockets in titanium parts, this article describes an effective approach to finishing internal corners.
Share




Hwacheon Machinery America, Inc.
Featured Content
View More



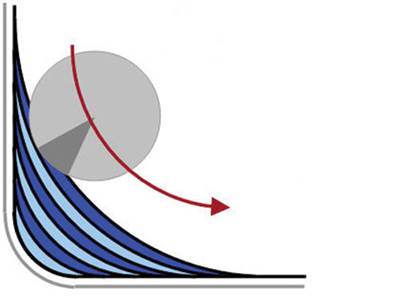
Though the “slicing” technique described in the article “Getting The Metal Out” (see Editor Picks at right) can be effective for roughing material from a corner in titanium, the considerations that go into finishing an internal corner go well beyond efficiency. Surface finish and part accuracy during the finishing pass also have to be considered—and both of these concerns are likely to be unmet if the same tool that finishes the walls of the pocket proceeds directly into the corners. When finish milling titanium, the corners have to be treated as an entirely separate operation, often performed before the finishing of the walls.
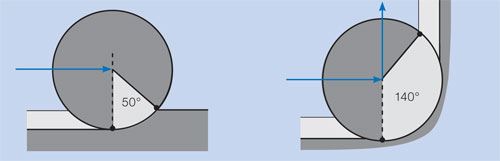
A drawing at right shows why. A milling tool running at a light radial depth of cut takes on a much heavier engagement as soon as it enters the corner. The tool is likely to both chatter and deflect in this area—assuming it even survives the increase in load.
One way to finish the corners separately and safely would be to slowly side mill just this material. Another approach would be to plunge mill the corner material. Both techniques might involve large length-to-diameter multiples because the tool can be no bigger than the specified radius of the internal corner. After evaluating both techniques at length-to-diameter multiples ranging up to 5.5, the Boeing Research and Technology group (BR&T) in St. Louis ultimately arrived at a corner machining process that combines plunging and side milling together.
Plunging corners is inherently more stable. Experiments showed this. Compared to side milling, plunge milling reduces tool deflection and considerably improves surface finish, while cycle time results showed the best improvement of all. However, plunging alone is insufficient. To clear enough material from the corners to leave ample clearance for the wall-finishing tools, Boeing recommends a technique called plunge-and-sweep. After plunging the corner, side milling can sweep out more of the material adjacent to the plunged area.
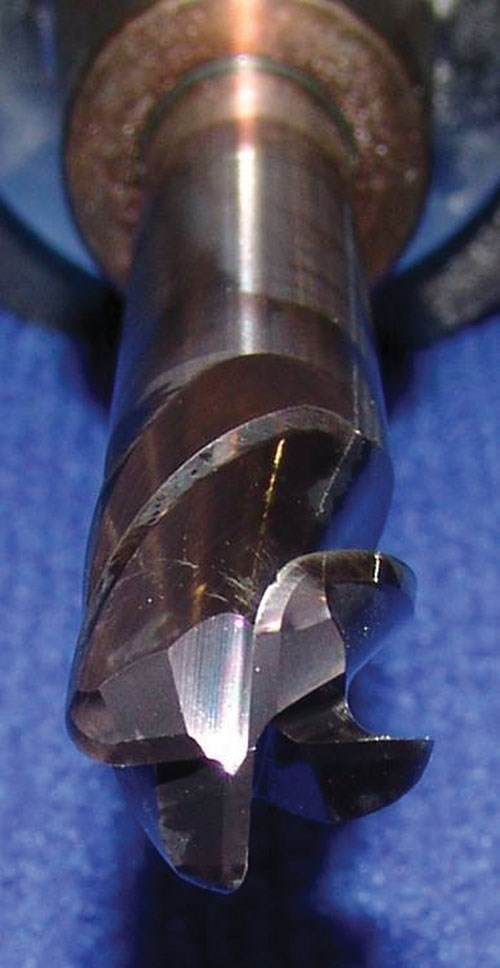
The same tool can be used for plunging and sweeping if the length-to-diameter ratio is no greater than 4. Above 4, Boeing says, only similar tools can be used. The plunging tool tends to chatter as it descends deep into the pocket. To overcome this, BR&T engineers use a tool with a stabilizing land of about 0.004 inch on each cutting edge. The land rubs against the part material, essentially stabilizing the cut by acting like a bearing surface. Because the same effect is counter-productive in side milling, a separate tool is needed for the sweep.
These separate plunge and sweep tools could actually be the same except for the land. The only disadvantage would be the chance for confusing the two tools because the land is not easy to see. The shop performing plunge-and-sweep might therefore prefer different numbers of flutes for the different operations—just for the value of being able to easily tell the two tools apart.
A final advantage of plunge-and-sweep is that it opens up the possibility for the sweep to be quite large—making room for a tool much larger than the internal corner to perform the finishing of the walls. Perhaps best illustrated by the 45-flute tool in the article about the 8-to-1 rule at right, a larger tool permits more flutes, which allows finishing to be performed at a higher feed rate. In this way, getting the corner material out of the way before wall finishing ultimately makes the overall finishing operation much more productive.
Editor’s note: You can read other parts in this series by clicking on Read Next (to the right).
Related Content
Sandvik Coromant Inserts Provide Stable Turning of Aerospace Components
The new insert grades GC1205 and GC1210 cover a large application area within last-stage machining and intermediate-stage machining when turning aerospace engine components.
Read MoreBavius Technologie Appoints New President, Schedules Technology Showcase
Roy D. Cripps will lead the team at Bavius as it aims to expand its current business in aerospace structures and develop new market segments. Additionally, the company will showcase its technology during an open house event on June 11.
Read MoreThe Role of Surface Finishing in Modern Manufacturing: Trends and Best Practices
You’re attending IMTS to advance your business. Regardless of your role in the manufacturing process, considering how your parts will be finished is crucial. This article can help you understand trends in surface finishing and better communicate with your finishing partners.
Read MoreHorizontal High-Speed Machining Saves Hundreds of Work Hours
High-speed machining is the latest change at Blair-HSM South, helping this once old-fashioned shop improve productivity and morale while enabling new work.
Read MoreRead Next
How To Machine Aircraft Titanium: Getting The Metal Out
Part of a series of articles on machining pockets in titanium parts, this article describes various options for roughing the hard metal efficiently.
Read MoreHow To Machine Aircraft Titanium: The 8-To-1 Rule For Finishing Walls And Ribs
Part of a series of articles on more efficient machining of pockets in titanium parts, this article makes the case for a tool with many cutting edges, and describes how best to apply it.
Read MoreHow To Machine Aircraft Titanium: Pricing The Process Instead Of The Tool
Part of a series of articles on more efficient machining of pockets in titanium parts, this article describes the importance of considering all of the costs that are affected by the choice of cutting tool.
Read More



































.png;maxWidth=300;quality=90)