Applying “Dengeling” to Finish Turbine Blades
This alternative to grinding, polishing and shot peening enables turbine blades to be machined and finished on one five-axis machine in one setup.
Share


Takumi USA
Featured Content
View More






Hwacheon Machinery America, Inc.
Featured Content
View More
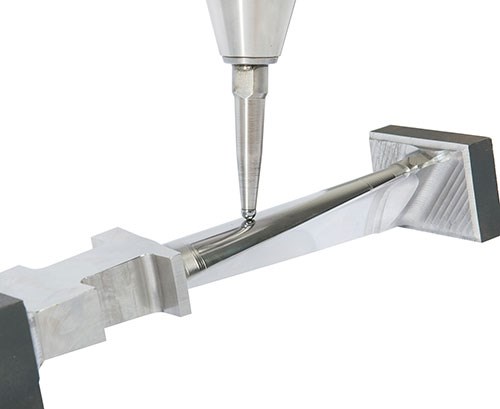
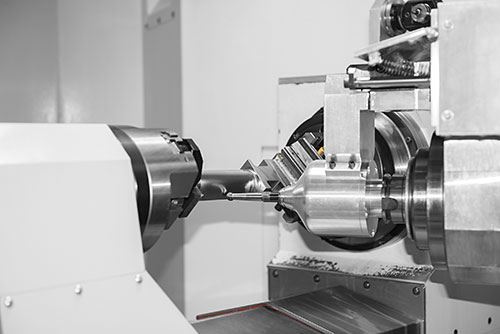
You might know “dengeln” (German for sharpening or honing) to be a manual process whereby a hammer and anvil are used to smooth and sharpen the blades of scythes or sickles. Today, a more advanced version of this concept is being applied to finishing turbine blades on the same five-axis machine that mills them.
Machine tool builder Starrag has developed what it calls its “dengeling” process for its LX series turbine blade machines to eliminate secondary polishing, grinding or shot peening operations, producing a ready-to-install blade in a single clamping. The technique can also eliminate manual polishing for dies and molds.
The dengeling process is performed after five-axis roughing and finish machining operations that create the blade profile. It uses an electrically powered head installed in the machine’s spindle that oscillates a tungsten carbide tool such that the tool’s spherical tip repeatedly impacts the blade at a rate as high as 600 Hz. As shown the video above, the process takes advantage of the five-axis movement provided by the machine (in this case, a Starrag LX 051 turbine blade machine). Dengeling cycle time is comparable to a finishing milling operation and delivers a surface finish of 0.2 micron Ra. The dengeling head can be stored in the machine’s toolchanger magazine like any other tool when not being used.
Michael Koller, Starrag product manager, says the dengeling process changes the original structure of the boundary layers on the part’s surface to a depth of 10 mm. As in a hardening process with quenching phase, a “distortion” of the atomic lattice occurs as the tool impacts the part. Therefore, the internal compressive stress (thus endurance strength) can be increased at specific areas of the part with precise control. The amount of increased hardness depends on the type of material (see Table 1), and the process can be applied on virtually every material that can be processed by means of plastic deformation.
The dengeling process is said to offer a number of blade performance advantages. In terms of material fatigue, crack initiation and propagation can be suppressed through the residual compressive stress that’s generated combined with the smooth surface. This differs from a grinding process that creates a smooth surface by simply cutting the scallops that remain following milling, because the surface cracks will remain. The dengeling process closes those cracks while compressing, hardening and smoothing the surface.
Material wear resistance can be significantly improved, too, because of higher surface hardness and better finish, while the threat of stress corrosion cracking commonly due to surface tensile strain is minimized. This means parts that are exposed to changing dynamic loads will have better fatigue resistance and a longer life.
Although shot peening is also widely used for finishing and hardening turbine blades, Mr. Koller says initial tests demonstrate that the dengeling process is more targeted and more controlled, with all programming performed using Starrag’s RCS 7 dedicated blade CAM system. Therefore, there is no need for covering or masking part areas that are not to be treated, and it is possible to hone critical thin areas at a blade’s edge more selectively.
Related Content
Inverting Turning and Five-Axis Milling at Famar
Automation is only the tip of the iceberg for Famar, which also provides multitasking options for its vertical lathes and horizontal five-axis machine tools.
Read MoreBuilding Machines and Apprenticeships In-House: 5-Axis Live
Universal machines were the main draw of Grob’s 5-Axis Live — though the company’s apprenticeship and support proved equally impressive.
Read MoreShoulder Milling Cuts Racing Part's Cycle Time By Over 50%
Pairing a shoulder mill with a five-axis machine has cut costs and cycle times for one of TTI Machine’s parts, enabling it to support a niche racing community.
Read MoreInside a CNC-Machined Gothic Monastery in Wyoming
An inside look into the Carmelite Monks of Wyoming, who are combining centuries-old Gothic architectural principles with modern CNC machining to build a monastery in the mountains of Wyoming.
Read MoreRead Next
5 Rules of Thumb for Buying CNC Machine Tools
Use these tips to carefully plan your machine tool purchases and to avoid regretting your decision later.
Read MoreSetting Up the Building Blocks for a Digital Factory
Woodward Inc. spent over a year developing an API to connect machines to its digital factory. Caron Engineering’s MiConnect has cut most of this process while also granting the shop greater access to machine information.
Read MoreRegistration Now Open for the Precision Machining Technology Show (PMTS) 2025
The precision machining industry’s premier event returns to Cleveland, OH, April 1-3.
Read More