Combining Absolute And Incremental Motions
While we agree that the absolute mode should be your positioning mode of choice for most applications, there are times when incremental mode can be quite helpful. Repeating motions within a subprogram, for example, is one excellent example.
Share





Hwacheon Machinery America, Inc.
Featured Content
View More



Autodesk, Inc.
Featured Content
View MoreWhile we agree that the absolute mode should be your positioning mode of choice for most applications, there are times when incremental mode can be quite helpful. Repeating motions within a subprogram, for example, is one excellent example. If you have six identical pockets to mill on a machining center or six identical grooves to neck on a turning center, you can save a lot of programming effort if you specify the motions to machine one pocket or groove incrementally. Repeating the commands renders another pocket or groove.
There are even times when it is helpful to command one axis move in the absolute mode while another moves in incremental mode. Any turning center using U and W to specify incremental motions in X and Z easily allows this. Say you're experiencing some unwanted taper on a diameter and you want to program a tapering movement to counteract the problem. In the command that turns the diameter that is experiencing unwanted taper, you can specify the Z endpoint in absolute mode from program zero and the X endpoint as an incremental departure. Here is an example:
N040 G01 U-0.002 Z-2.5 F0.005
In this command, the tool will move 0.001 inch in the X minus direction (a 0.002-inch diameter change) while the Z axis moves to an endpoint of minus 2.5-inch relative to program zero.
Though it's not common knowledge, many current model machining center controls actually allow you to specify one axis in the absolute mode in the same command as an incremental departure in another axis. This is one time when the word order within a CNC command is important. Consider this machining center command:
N060 G00 G90 X4.5 G91 Y1.0
It will rapid the control to an X position of 4.5 inch (relative to program zero) at the same time it moves the Y axis in the positive direction by one inch. If you are in doubt as to whether your control allows this, it's easy enough to set up a test program to find out. Simply repeat the command just given a few times in a program. After the initial XY motion, each subsequent command should cause no motion in the X axis, while the Y axis moves plus one inch per command in Y.
At first glance, you may question when this method could ever be helpful. Consider a horizontal machining center that has a rotary axis. It's often helpful during approach movements to rotate the rotary axis to its first position during the X and Y approach. Since you almost always program X and Y approach movements in the absolute mode, you're likely having to specify rotary axis motion in the absolute mode as well. Or worse, you're breaking the motion into two commands, one to approach in XY and another to approach in the rotary axis. Consider this horizontal machining center approach command:
N075 G00 G90 X2.5 Y3.0 G91 B-90.0
It tells the control to move in X and Y relative to program zero (absolute mode) while the rotary axis moves in the minus direction by 90 degrees. This can really simplify the programming of the rotary axis when it's being used as an indexer. Note that at the completion of this command, most controls will be in the incremental mode, meaning the next command must include a G90 if you expect to work from program zero.
Related Content
The Power of Practical Demonstrations and Projects
Practical work has served Bridgerland Technical College both in preparing its current students for manufacturing jobs and in appealing to new generations of potential machinists.
Read More5 Tips for Running a Profitable Aerospace Shop
Aerospace machining is a demanding and competitive sector of manufacturing, but this shop demonstrates five ways to find aerospace success.
Read MoreHow to Mitigate Chatter to Boost Machining Rates
There are usually better solutions to chatter than just reducing the feed rate. Through vibration analysis, the chatter problem can be solved, enabling much higher metal removal rates, better quality and longer tool life.
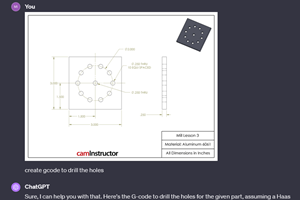
Read MoreCan ChatGPT Create Usable G-Code Programs?
Since its debut in late 2022, ChatGPT has been used in many situations, from writing stories to writing code, including G-code. But is it useful to shops? We asked a CAM expert for his thoughts.
Read MoreRead Next
Building Out a Foundation for Student Machinists
Autodesk and Haas have teamed up to produce an introductory course for students that covers the basics of CAD, CAM and CNC while providing them with a portfolio part.
Read More5 Rules of Thumb for Buying CNC Machine Tools
Use these tips to carefully plan your machine tool purchases and to avoid regretting your decision later.
Read MoreRegistration Now Open for the Precision Machining Technology Show (PMTS) 2025
The precision machining industry’s premier event returns to Cleveland, OH, April 1-3.
Read More
.jpg;width=70;height=70;mode=crop)





























.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)






.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)