Share





Does the music industry have a lesson to teach manufacturing?
Stephan Thomas says yes, and the lesson is partly a cautionary tale. The music industry lost more than half its value after the onset of free digital sharing of music around 2000. Only when the industry found platforms for sharing data but also keeping that data secure (Spotify, for example) did its sales begin to grow again. Mr. Thomas is co-founder of a company, Identify3D, that aims to bring the same kind of data security to manufacturing.
The music analogy goes only so far, he says, because the peril in manufacturing is significantly greater. If a stolen music file is misused, only the listening experience will suffer. However, if a stolen part file is manufactured in ways that the originator of that file did not intend, it will result in not only lost revenue, but also counterfeit parts of lower quality potentially finding their way into the supply chain.
For critical parts, the way that buyers for those parts generally guard against this danger today is through tightly controlled relationships with suppliers. That is, suppliers are vetted and frequently certified by the OEM buyer. This effort is costly, and that cost finds its way into the final product. Identify3D offers what it expects manufacturing buyers will see as a cheaper alternative: digital rights management that restricts not only the access to a CAD file, but also the manufacturing choices that can be associated with it.
“Our vision is to be like PDF for manufacturing,” Mr. Thomas says, “essentially an easily usable standard available everywhere manufacturing is done.” Formerly with Ernst & Young, Mr. Thomas’s experience is in manufacturing supply chains. The company’s other co-founder, Joe Inkenbrandt, has a background in security and cryptography.
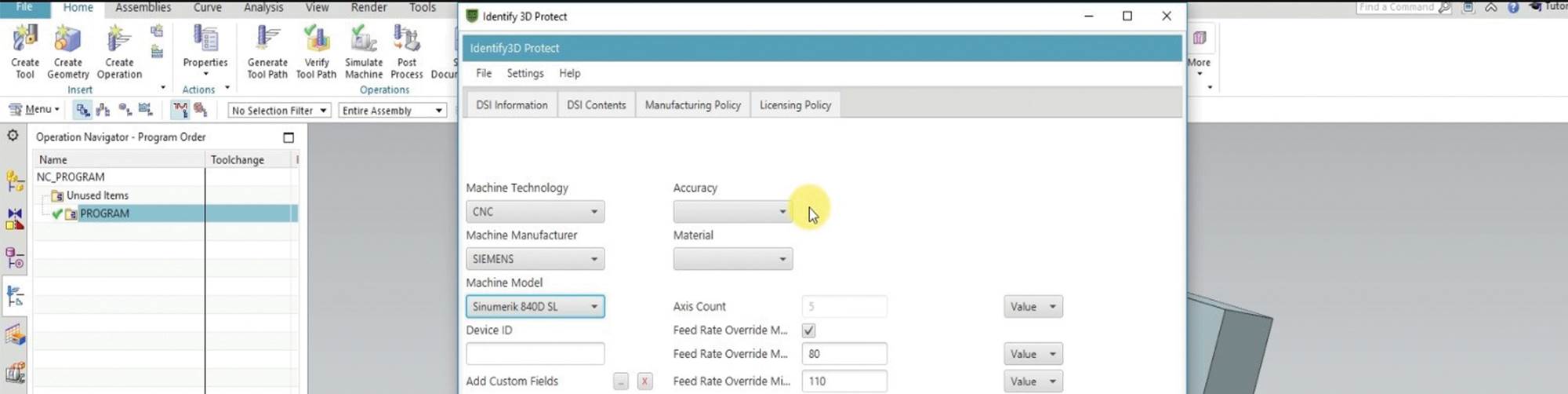
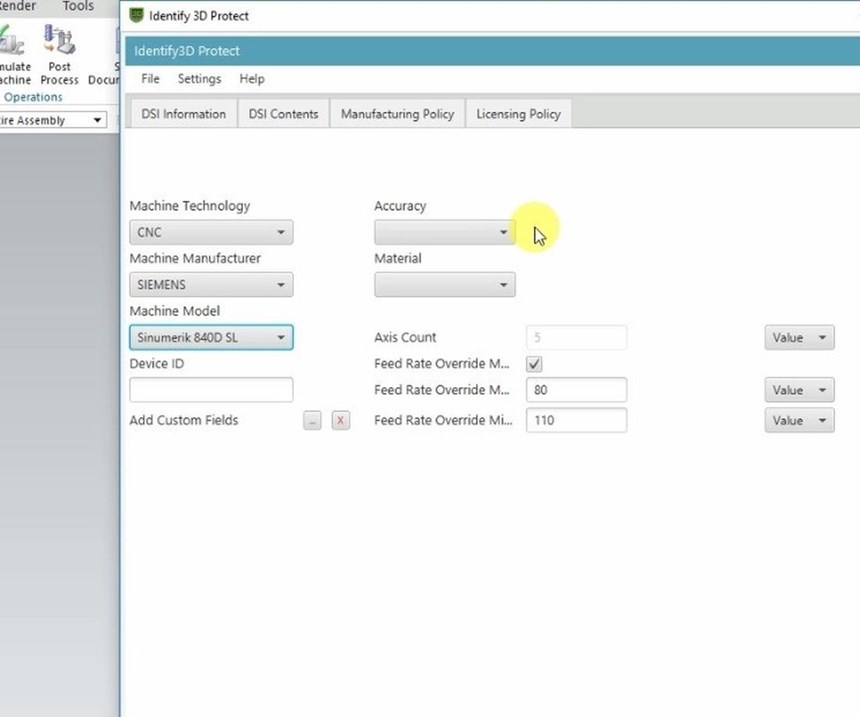
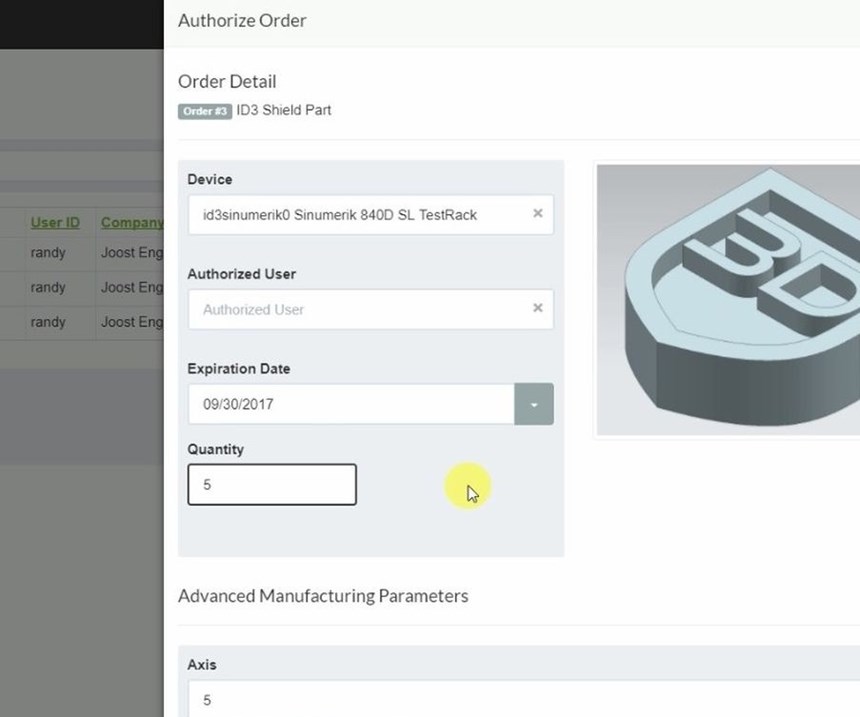
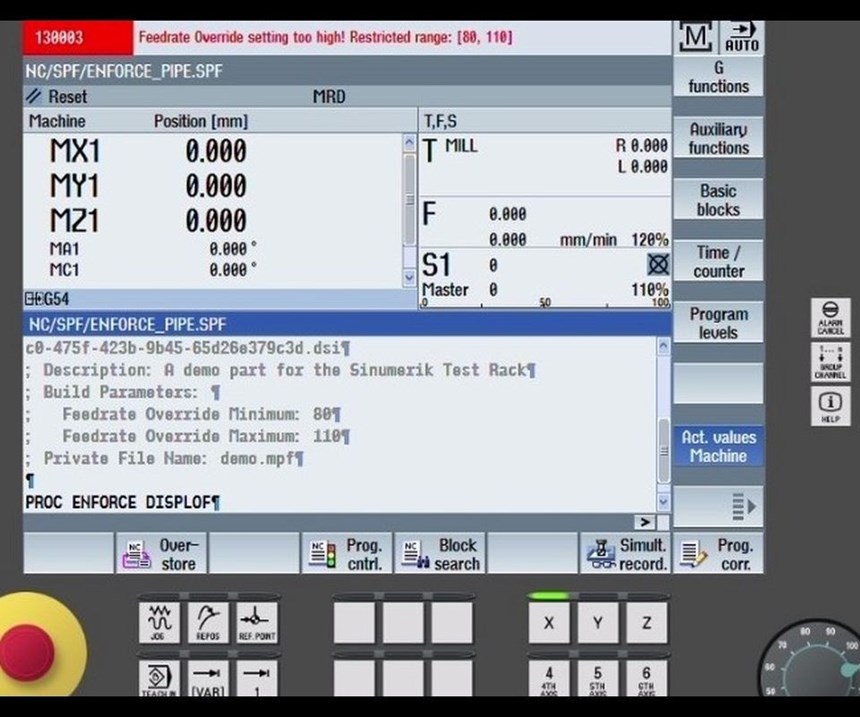
Like a PDF file, a CAD file that is protected using Identify3D would be opened—and could only be opened—using a software utility at the receiving end. In a machine shop, this software could run on the machine’s CNC or (for older machines) on a PC networked to the control. The utility can protect access, but it also does more than that. It enables the file’s originator to place manufacturing-related restrictions on the model. The number of parts the file can be used to produce can be limited. Restrictions can also control the type of machine used to make the part and the parameters at which machining passes are run. That is, details a sensitive OEM might control through on-site certification can now be controlled remotely through software. In this sense, the system empowers the OEM.
But in another sense, the system also empowers manufacturing suppliers, Mr. Thomas says. Being personally engaged with the OEM and being successfully admitted to an OEM’s certified supplier list no longer have to be requirements for carrying out a given company’s work. With both the part and its process protected, it is easier for OEMs to give work to suppliers that are strangers to them.
Siemens recently announced its partnership with Identify3D, in which it will integrate the digital rights management system into its Sinumerik CNCs and into its Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) software. Also listed as partners by Identify3D are additive manufacturing companies including EOS, Materialise and Renishaw. Additive manufacturing is a particularly important area for file security, Mr. Thomas says. In additive, there are more parameters directly available at the machine control, and therefore, more parameters that can be defined and controlled at a distance. In addition, an effective additive manufacturing process for a given part is frequently the result of considerable trial and error, and some of the manufacturing process considerations discovered as a result (such as part orientation and support structure design) are directly apparent in the model. Therefore, in additive, the part file to be protected includes not just design details, but also intellectual property related to manufacturing that has to be guarded as well.
Related Content
Can AI Replace Programmers? Writers Face a Similar Question
The answer is the same in both cases. Artificial intelligence performs sophisticated tasks, but falls short of delivering on the fullness of what the work entails.
Read MoreTips for Designing CNC Programs That Help Operators
The way a G-code program is formatted directly affects the productivity of the CNC people who use them. Design CNC programs that make CNC setup people and operators’ jobs easier.
Read MoreThe Power of Practical Demonstrations and Projects
Practical work has served Bridgerland Technical College both in preparing its current students for manufacturing jobs and in appealing to new generations of potential machinists.
Read More5 Tips for Running a Profitable Aerospace Shop
Aerospace machining is a demanding and competitive sector of manufacturing, but this shop demonstrates five ways to find aerospace success.
Read MoreRead Next
5 Rules of Thumb for Buying CNC Machine Tools
Use these tips to carefully plan your machine tool purchases and to avoid regretting your decision later.
Read MoreBuilding Out a Foundation for Student Machinists
Autodesk and Haas have teamed up to produce an introductory course for students that covers the basics of CAD, CAM and CNC while providing them with a portfolio part.
Read MoreRegistration Now Open for the Precision Machining Technology Show (PMTS) 2025
The precision machining industry’s premier event returns to Cleveland, OH, April 1-3.
Read More