Fill the Night Shift with a Machine-Tending Cobot
When a large order necessitated adding a third shift, Toolcraft was having trouble hiring anyone to cover it. By investing in a UR5e collaborative robot from Universal Robots, the shop quickly achieved 24/7 production as well as time savings and increased throughput.
Share





After Rapid Design Solutions’ Troy Ojalehto (left) developed the initial application, Toolcraft’s automation engineer Brian Laulainen was able to handle the daily operation in addition to developing a parts rinsing and drying station as an application add-on for the UR5e, a cobot from Universal Robots. Mr. Laulainen did the training through UR Academy, then supplemented with a few hours of hands-on training with Mr. Ojalehto.
Toolcraft, a small machine shop in Seattle, needed to automate a challenging, three-operation machine tending task within its CNC machine. Impressed with Universal Robots’ (UR) new flagship cobot, the UR5e, and its 30-micron repeatability and force/torque sensing capabilities, the shop took on the task and saved 23% on production costs and increased throughput 43%.
The critical moment that prompted this move came when a large order prompted Toolcraft to add a third shift for 24/7 production. “Nobody wants to run on third shift around here,” says Steve Wittenberg, director of operations. In an area with 3% unemployment, the shop was not getting much response to its help wanted ad. He started looking at different automation options, initially considering traditional industrial robots.
Looking solely at hardware, it seemed like traditional robots, would be the more cost-effective solution, Mr. Wittenberg says. “But once we started factoring in the savings on not having to erect a safety cage — and the time saved on the ease of use, avoiding a lot of complex programming — Universal Robots ended up being the right solution.”

This multi-threaded medical device component required high precision and three-step handling inside the machine tool, necessitating the addition of a third shift. Toolcraft’s solution was to hand over machine tending to a collaborative robot, the UR5e.
Cobot Works the Night Shift
The order spurring this investment was for a multi-threaded part for a medical device. This part needed to be loaded into a three-step CNC machining operation that would run during a third shift. Toolcraft discussed the challenge with Rapid Design Solutions, a certified systems integrator of Universal Robots.
“When you’re doing multi-operation precision machining, the accuracy requirements go way up,” says Rapid Designs Solutions owner Troy Ojalehto. “When we heard that the repeatability of the UR5e was down to 30 microns, we were very excited. That really competes in the same space as traditional industrial robots, so that was huge for us. I have not seen other cobots handling this level of precision with multi-operation parts like this, with raw stock going in and completed precision parts coming out.”
Six months after implementation, Mr. Wittenberg says that the shop saw a production increase right away. “We were able to staff that third shift and went from producing 255 parts a week to 370 parts per week. Along with that, we were able to finish our year’s production seven weeks early, thus freeing up that machine to produce parts for other jobs.”
He adds Toolcraft is looking at an ROI of about 12 months.

“The UR’s free-drive function greatly reduces the time to teach robot points,” Mr. Ojalehto says. UR cobots can easily be programmed through the teach method by simply moving the arm through desired waypoints that are added to the program on the teach pendant. When the cobot was in use, Toolcraft used the UR simulator to create the entire program for the parts rinsing and drying station offline, inserting the waypoints as they transferred the program to the teach pendant.
Cobot Cleans Up
While the cobot successfully helped the shop implement 24/7 production, the cobot was still not working to its full potential. The machining cycle lasts a total of 56 minutes, but the UR5e is only busy tending parts for six minutes. “The rest of the time, the cobot was just hanging out waiting for the next cycle. We wanted to keep it busy,” Mr. Wittenberg says. To occupy more of the cobot’s time, the shop added a part rinsing and cleaning station.
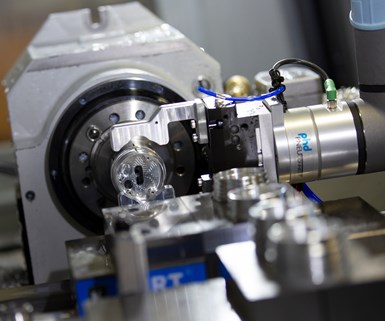
Featuring 30-micron repeatability, the UR5e was able to precisely insert the multi-threaded part into the fixturing. The CNC cycle includes three operations in a vertical machining center: two in vise fixtures and one in a fourth-axis rotary unit.
As the UR5e takes the machined part out of the CNC, it dips the part into a rinsing solution, passes it through an air jet, and places the washed and dried part on a rack for shipping. The machine shop was also able to control the pneumatic fixture and door actuators through the UR5e I/O interfaces. “This greatly reduces the need for CNC wiring and preserves all the CNC’s standard safety functions,” Mr. Ojalehto explains.
Learning to Program
While Toolcraft enlisted the assistance of a system integrator to get the initial application up and running, the machine shop was able to program and install the rinsing and drying station on its own. “What really enabled us to do this was all the free online support Universal Robots gives you,” Mr. Wittenberg says. “After our automation engineer took the online UR Academy course, he spent a few hours with the integrator and was able to add that station to the cobot cycle.”
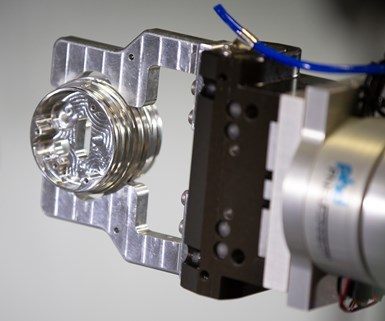
Toolcraft chose the PneuConnect gripper from PHD as end-of-arm-tooling for the UR5e. Being UR+ certified means the gripper is certified to work seamlessly with UR cobots, with all programming software integrated directly on the UR cobot’s teach pendant.
“We had zero experience with robots at Toolcraft,” says Brian Laulainen, Toolcraft’s automation engineer. “UR Academy was a very intuitive, interactive and fun course to take. It made learning a lot more interesting than just reading a book.”
At first, Mr. Wittenberg feared that production would go down during the rinsing station’s programming phase since the cobot would be pulled away from its regular machine-tending duties. The team discovered, however, that they could use Universal Robots’ simulator and program almost the entire addition to the cycle offline while the cobot kept working. The offline program is simply loaded via USB directly into the UR5e’s teach pendant. “In the program I did in my office, I’d just set blank waypoints. Once I was next to the cobot, I was able to quickly use the free-drive motion and move the robot into the correct positions and teach the new waypoints,” Mr. Laulainen says.

With the UR5e, Toolcraft was able to finish its annual production seven weeks sooner than with manual labor.
Another Year, Another Cobot
With the first successful cobot installation under its belt, Toolcraft is now planning to install one additional cobot every year going forward. “The fact that our own automation engineer is now able to go in and troubleshoot anything that comes up is going to be key to meeting this goal,” Mr. Wittenberg says. The next task he expects to be automated on the shop floor is tending a horizontal machining center. “That’s a potential challenge, because the mill uses rotary tombstones that are swapped in and out of the milling machine, which creates some difficulties with fixturing. But we’re confident we can solve those issues using a Universal Robot and some innovation in fixturing.”
Related Content
Four-Axis Horizontal Machining Doubles Shop’s Productivity
Horizontal four-axis machining enabled McKenzie CNC to cut operations and cycle times for its high-mix, high-repeat work — more than doubling its throughput.
Read MoreLean Approach to Automated Machine Tending Delivers Quicker Paths to Success
Almost any shop can automate at least some of its production, even in low-volume, high-mix applications. The key to getting started is finding the simplest solutions that fit your requirements. It helps to work with an automation partner that understands your needs.
Read MoreSame Headcount, Double the Sales: Successful Job Shop Automation
Doubling sales requires more than just robots. Pro Products’ staff works in tandem with robots, performing inspection and other value-added activities.
Read MoreCutting Part Programming Times Through AI
CAM Assist cuts repetition from part programming — early users say it cuts tribal knowledge and could be a useful tool for training new programmers.
Read MoreRead Next
5 Things to Consider Before Purchasing a Robot
Start simple, and you’ll be successful.
Read MoreIncreasing Employee Output Through Automation: Here is What We Found in 7 Recent Shop Visits
Modern Machine Shop editors routinely visit machining facilities to report on shops that are succeeding. Here is what our editors found on seven recent shop visits, all related to using labor more efficiently.
Read MoreIs Robotic Automation the Key to Drawing (and Keeping) New Employees?
Robotic automation is transforming a job that was perhaps a machine operator’s least-favorite work assignment into one that is not a heavy lift.
Read More






























