Share




Electric current often outperforms physical media in fine finishing operations. However, CNC machine shops considering electropolishing must be careful to ensure metal parts retain sufficient levels of stock.
According to Chicago-area service provider Able Electropolishing, this non-contact, fine-finishing process generally removes between 0.0005 and 0.001 inch of material. How much depends on a manufacturer’s goals, which might range from achieving a certain roughness average (Ra) value, a shiny finish, micro-burr removal, and/or passivation for improved resistance to corrosion, contaminants or fatigue. Manufacturers should also keep in mind that electropolishing material removal can be controlled to within 0.0001 to 0.0002 inch. Adding this range to machining tolerances can provide a general indication of how much stock to leave after machining
However, achieving the desired result requires thinking deeper than these general guidelines. Other considerations include:
Machining Specifications
Electropolishing service providers must understand which areas of a part require the most precision because electropolishing is an indiscriminate material remover. Racks of workpieces, positively charged to serve as anodes, are bathed in an electrolyte solution along with negatively charged cathodes. DC current flowing from anode to cathode draws minute fragments of material away from all part surfaces at once. Depending on geometry and other part characteristics, current density at any given point on the surface can vary. As a result, some areas of the rack-mounted parts can shed more material than others. Designing fixtures that ensure uniform current density and avoid leaving critical features undersized — the true art of electropolishing — requires pre-production sampling.

Material
Pre-production sampling is also critical for revealing how different alloy formulations react to the process. Alloys suitable for electropolishing include aluminum formulations, brass, copper materials, carbon steel, titanium, and nickel- and tungsten-based metals. Generally, alloys require removing more stock than non-alloys to achieve the desired result, but precise levels depend heavily on the specifics of the material formulation. For instance, a failed salt-spray corrosion-resistance test after sampling might lead a manufacturer to choose an alternative composition.

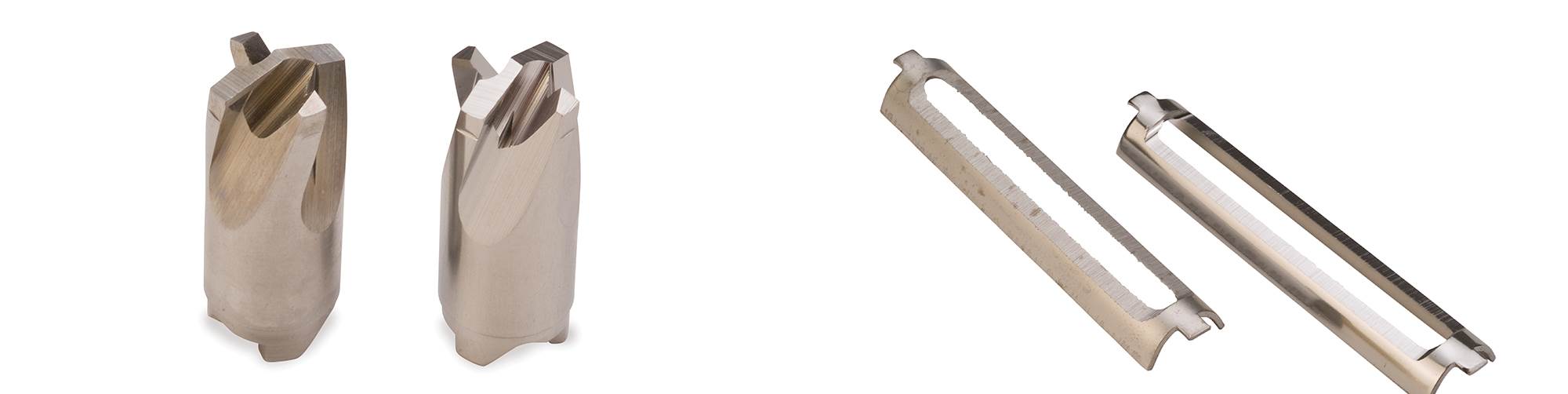
Here is a vegetable peeler blade before and after electropolishing.
Desired Surface Characteristics
To say that electropolishing provides a “smooth, shiny surface” would be accurate, but it is important to distinguish between those two terms. Electropolishing’s effect on a part’s shininess, or brightness, is affected primarily by the material’s chromium-to-iron ratio. However, a part can appear shiny without being smooth. Ra, a common a measure of smoothness, is defined by the average distance between the microscopic peaks and valleys that constitute all surfaces. Electropolishing creates a leveling effect (thus reducing Ra and making the surface smoother) by shaving the peaks. The slower and more controlled the process, the smoother the resulting surface. However, not all shiny parts must be smooth. Manufacturers must be clear about their goals from the outset.
Stock Level Limits
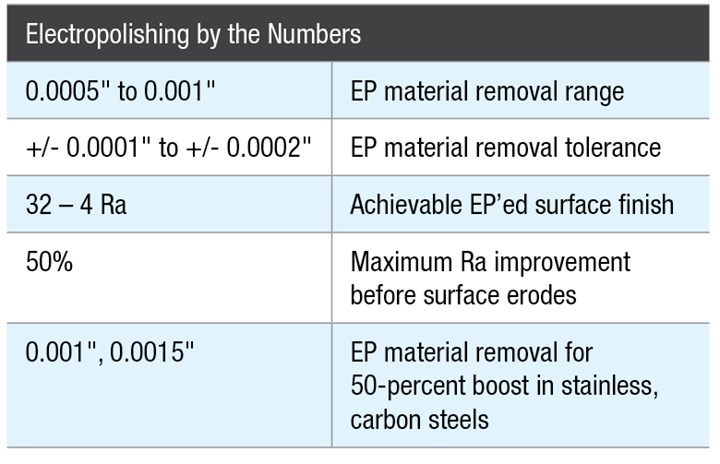
Generally, the more stock removed, the better the results of electropolishing, but only to a certain point. Once a surface’s peaks have been shaved away, the current begins to cut into valleys as well. The surface begins to erode and become rougher rather than smoother.
What does this mean for CNC machine shops? The smoother the part is prior to finishing, the better the result that can be achieved with electropolishing For example, according to the 50-percent guideline in the chart above, 16 Ra is the best possible result with a part that has been machined to 32 Ra. If specifications call for 8 Ra, the part would have to be ground, or undergo some other finishing process, to achieve at least 16 Ra first.
Based on an article by Scott Potter, vice president of sales at Able Electropolishing Co.
Related Content
Vollmer Ultrasonic Cleaning, Deburring System Provides Process Reliability
IMTS 2024: The UltraTec Ultrasonic A25 cleans and deburrs small and delicate components, making it well suited for applications in heavily regulated sectors with challenging demands.
Read MoreHow to Accelerate Robotic Deburring & Automated Material Removal
Pairing automation with air-driven motors that push cutting tool speeds up to 65,000 RPM with no duty cycle can dramatically improve throughput and improve finishing.
Read MoreTapmatic Showcases Deburring Tool for a Consistent Edge Break
IMTS 2024: Tapmatic Corp. exhibits the DeBurr-Z deburring tool for simplified programming and a consistent edge break.
Read MoreMastercam Software Improves Programming Flexibility
IMTS 2024: Mastercam introduces Mastercam 2025, with features including Mastercam Deburr for automated edge finishing, finish passes, mill-turn support for Y-axis turning and automatic license update notifications.
Read MoreRead Next
What Is Electropolishing?
Able Electropolishing produced this video to explain the electropolishing process, which is used for microfinishing, fatigue life improvement and even deburring in cases where the part is too delicate for more forceful finishing methods.
Read MoreUnderstanding Electropolishing
Compared to other options for deburring high volumes of metal parts, this process is said to be particularly well suited for the smallest imperfections and most fragile workpieces.
Read MoreBuilding Out a Foundation for Student Machinists
Autodesk and Haas have teamed up to produce an introductory course for students that covers the basics of CAD, CAM and CNC while providing them with a portfolio part.
Read More























.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)