Arcing away from Near-Net Forging
An electrical arc process joins a field of additive manufacturing technologies that could one day provide aerospace manufacturers with alternatives to near-net-shape forgings.
Share




In the future, pounding heated metal into submission will not be the only viable means of producing certain near-net-shape aerospace components. According to various suppliers, additive manufacturing technology continues to progress toward the same standards for material strength and reliability as forging. They also claim that these freeform deposition processes take less time than forging (a matter of hours for larger components) and bring parts even closer to final geometry. By eliminating the need for tooling and reducing the time and cost required for finish-machining, these forging alternatives promise to compress the front end of the development cycle, reduce the overall production cost of aerospace structural components, and, eventually, facilitate new part designs that would not be feasible with forging.
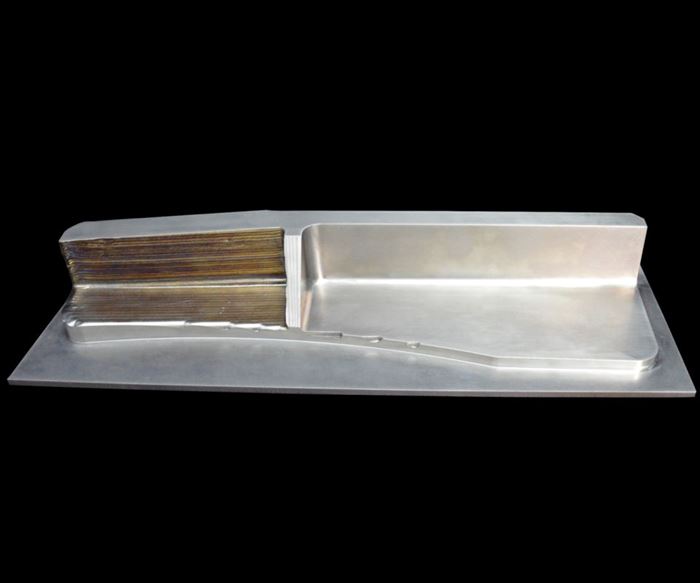
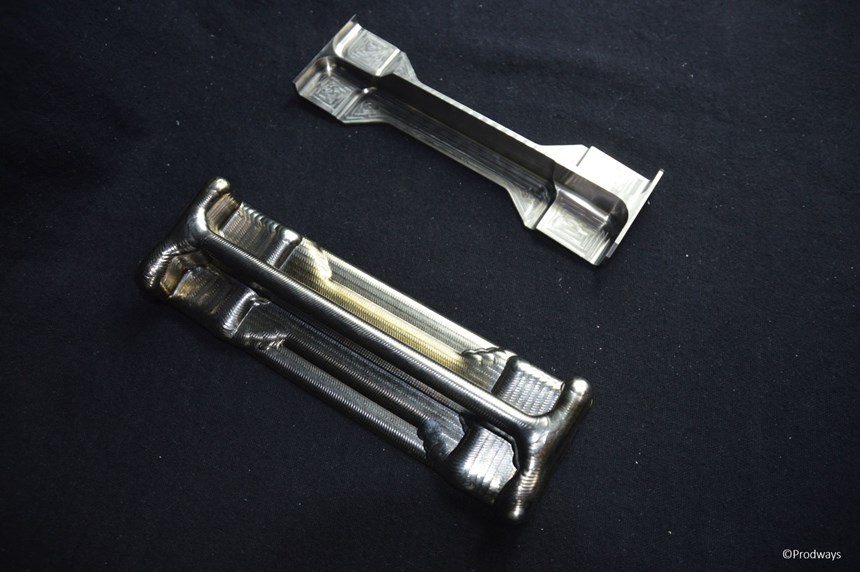
One of the most recent examples, Rapid Additive Forging (RAF) technology, offers cost savings ranging from 30 to 50 percent on various titanium parts, says Olivier Strebelle, deputy chief executive officer of strategy and business development at Groupe Gorgé, the parent company of RAF technology developer and fellow French firm Prodways. Similar to other metal deposition techniques, the deposition head and the wire material feedstock move together throughout the workzone. Unlike processes that build geometry up from beds of powder, the only restriction on part size is the travel limit of the deposition head, Mr. Strebelle says. Although final forms are not as detailed as those produced via powder-bed sintering, they’re more than detailed enough to replace forgings. Metal deposition processes are faster than powder-bed technologies, too.
One of the primary areas in which these freeform material deposition techniques differ is the means of melting the material. RAF uses an electric arc similar to the technology employed by gas-metal-arc welding systems, and testing so far has focused primarily on titanium. The deposition head travels on a robot from Commercy Robotique, another subsidiary of Groupe Gorgé, within an enclosed atmosphere of inert gas. Initial testing shows potential speed advantages compared to laser systems because more power is available, Mr. Strebelle says. As for electron-beam sintering systems, “Our assessment is that arc-based technologies are more robust,” he continues. “This is based on our welding experience, where arc-based robots are more reliable.”
However, he emphasizes that the process is still maturing. Engineers are still working toward matching the highest standards of forged-part tensile strength, porosity and other properties. Still, they are getting close. “It could work already for parts that are not of the highest class,” he says, adding that proving the process out for flight-ready parts is likely only a matter of time. In fact, at the time of this writing, Prodways was reportedly working with an aerospace client to qualify parts that could be flying by 2019. New materials, such as aluminum and Inconel, will also undergo further testing. The company is also considering how a RAF system for production might look different than one for prototyping, and how the process might be better integrated with machining, possibly via a hybrid additive/subtractive machine. Size capabilities will most certainly expand, he says, with the next generation systems’ increasing the limit from 70-cm to 3-meter parts.
All of this work is being conducted in Europe, but Mr. Strebelle says the company could easily supply blanks produced via RAF technology from its North American headquarters in Minneapolis, Minnesota. As the process matures, he says the technology will likely follow the same path as the company’s other, mostly plastics-focused additive manufacturing offerings, with Prodways eventually moving to offer the RAF systems themselves in addition to RAF production services.
Related Content
How a Custom ERP System Drives Automation in Large-Format Machining
Part of Major Tool’s 52,000 square-foot building expansion includes the installation of this new Waldrich Coburg Taurus 30 vertical machining center.
Read MoreIncreasing OEM Visibility to Shopfloor Operations for the Win
A former employee of General Motors and Tesla talks about the issues that led to shutdowns on factory lines, and what small- to medium-sized manufacturers can do today to win business from large OEMs.
Read MoreBavius Technologie Appoints New President, Schedules Technology Showcase
Roy D. Cripps will lead the team at Bavius as it aims to expand its current business in aerospace structures and develop new market segments. Additionally, the company will showcase its technology during an open house event on June 11.
Read MoreRego-Fix Appoints New Global Aerospace Specialist
Sherman D’Souza will provide global customers with access to Rego-Fix research, development and technical support teams to create and supply toolholding solutions.
Read MoreRead Next
5 Rules of Thumb for Buying CNC Machine Tools
Use these tips to carefully plan your machine tool purchases and to avoid regretting your decision later.
Read MoreBuilding Out a Foundation for Student Machinists
Autodesk and Haas have teamed up to produce an introductory course for students that covers the basics of CAD, CAM and CNC while providing them with a portfolio part.
Read MoreSetting Up the Building Blocks for a Digital Factory
Woodward Inc. spent over a year developing an API to connect machines to its digital factory. Caron Engineering’s MiConnect has cut most of this process while also granting the shop greater access to machine information.
Read More