Tips for Anticipating Hole Conditions
When measuring an ID with an indicating plug gage, it is OK to slow down to learn more about the hole being measured and explore for extraneous conditions.
Share




Takumi USA
Featured Content
View More



ECi Software Solutions, Inc.
Featured Content
View More
Hwacheon Machinery America, Inc.
Featured Content
View More
For most users, a fixed-body indicating plug gage, whether mechanical or pneumatic, is probably the easiest gage to use to get a fast, high-precision and accurate hole diameter. Simply insert the plug gage into the hole and read the deviation from the master to get the diameter.
However, the real advantage of these types of gages over an adjustable bore gage is that it is a lot easier and faster to determine hole conditions such as ovality, taper, hourglass or bell-mouth shape. All it takes is a further exploration of the bore.
The need for speed is certainly the cry of production manufacturing, but when measuring an ID with an indicating plug gage, it is OK to slow down just a little to learn more about the hole being measured. Take the time to explore for extraneous conditions, and should something be discovered, find the minimum diameter, as it generally will have the greatest effect when a shaft or cylinder is assembled to the bore.
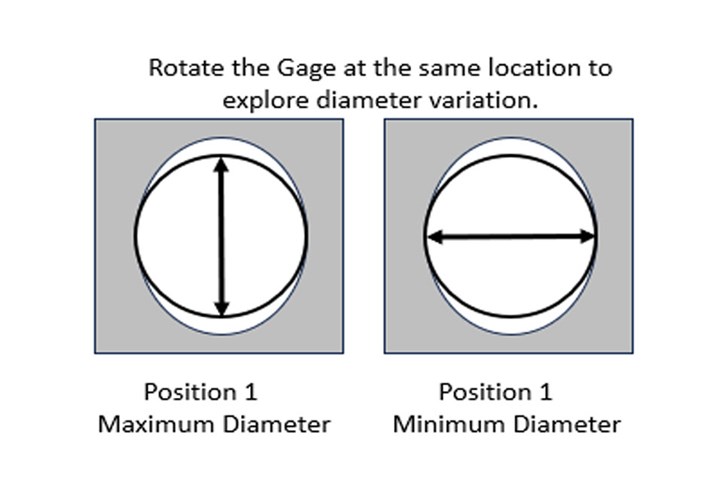
First, simply rotate the plug at the same level in the bore, searching for the minimum and maximum conditions. This is easy to follow on an analog scale.
Hopefully, both readings are within the diameter tolerance. If not, this could indicate that something is awry with the manufacturing process. As mentioned above, it is probably a good idea to note specifically where the minimum diameter is located, as it may help fix or prevent future problems.
This diameter variation — the difference between the minimum and the maximum diameters — is often referred to as total indicator runout (TIR). With many digital indicators or bench amplifiers, there are built-in functions that can be used to “remember” this difference, so the operator does not have to manually calculate it.
Some confuse TIR with “roundness.” This is not the case; true roundness is different and defined in various international standards. However, some will use TIR at the point of manufacture as a trigger point for further measurements if the variation becomes significant compared to the diameter tolerance.
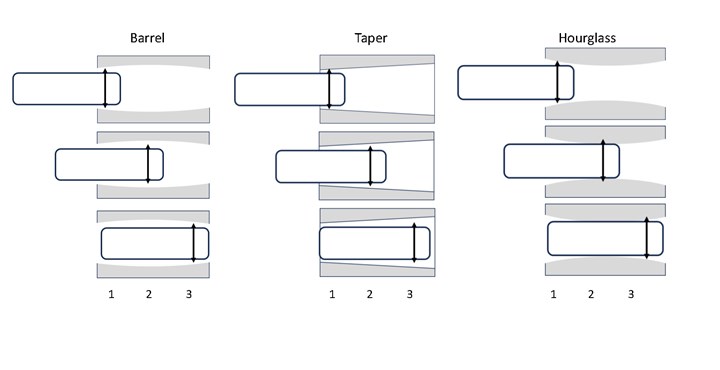
The next step in learning more about the hole is to start exploring it axially, say at three points along the length of the bore, and compare the three diameters. By comparing these diameters, it becomes easy to identify the presence of an hourglass, bell mouth or taper within the form of the hole.
As the figure below illustrates, the fixed plug gage can disclose these conditions with exploration at different depths. All of these are apt to appear within every hole manufactured, but the degree of the form error compared to the diameter tolerance is most important.
By exploring the hole axially at multiple locations, form errors such as hourglass, barrel or taper can be found. Photo Credit: Mahr Inc.
Some users will check these types of parts both radially and axially, exploring for the minimum and maximum values — or an overall diameter variation. As with Roundness, some might say this exploration is an indication of cylindricity. Cylindricity is a well-defined form parameter, and our exploration would not be the proper way to check this. However, use this as a trigger for further analysis if the variation is a large part of the diameter tolerance.
These small deviations in form are very critical in machine design, where surface contact is required for a shaft, and bearing is required. Conditions like the ones above would result in very uneven loading on the parts, which ultimately leads to vibration, faster wear and even premature breakdown. Taking a little extra time to explore critical components with a fixed plug bore gage can help to prevent these conditions.
But what if — even after a close inspection of the diameter and a thorough exploration of the part — there are some mating issues with the hole and its shaft? This may come down to other form errors where the two-point fixed plug gage just cannot measure.
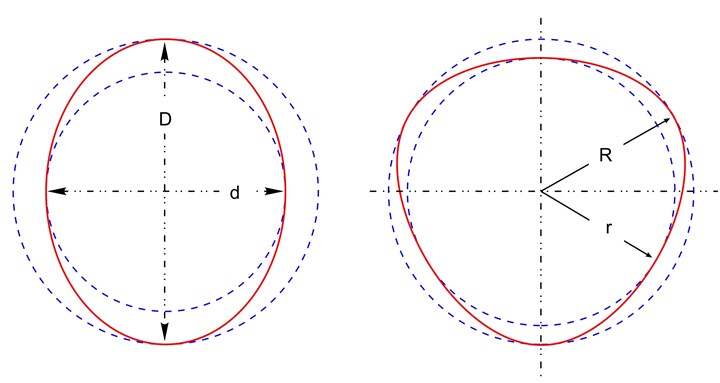
A two-point fixed plug gage is great for inspecting for a minimum and a maximum diameter, as shown in the first figure above. The figure shows a hole that has two lobes; thus, it is a hole with an even number of lobes. A two-point plug can easily find this diameter variation.
But try to measure a hole that has an odd number of lobes — three, for example — and the gage is apt to show the part at the correct diameter and to have very little diameter for form variation. This is because a two-point plug gage cannot measure this condition.
A two-point gaging system is best for even lobbing conditions, while a three-point gaging system is best for odd lobbing conditions. Photo Credit: Mahr Inc.
A fixed plug gage can provide more information about a hole than just the diameter at a single location. By making an effort to explore the hole, further details about the part shape can be made, as well as potential problems with mating parts.
Related Content
4 Ways to Establish Machine Accuracy
Understanding all the things that contribute to a machine’s full potential accuracy will inform what to prioritize when fine-tuning the machine.
Read MoreThe Many Ways of Measuring Thickness
While it may seem to be a straightforward check, there are many approaches to measuring thickness that are determined by the requirements of the part.
Read MoreProcess Control — Leveraging Machine Shop Connectivity in Real Time
Renishaw Central, the company’s new end-to-end process control software, offers a new methodology for producing families of parts through actionable data.
Read MoreChoosing the Correct Gage Type for Groove Inspection
Grooves play a critical functional role for seal rings and retainer rings, so good gaging practices are a must.
Read MoreRead Next
Building Out a Foundation for Student Machinists
Autodesk and Haas have teamed up to produce an introductory course for students that covers the basics of CAD, CAM and CNC while providing them with a portfolio part.
Read More5 Rules of Thumb for Buying CNC Machine Tools
Use these tips to carefully plan your machine tool purchases and to avoid regretting your decision later.
Read MoreRegistration Now Open for the Precision Machining Technology Show (PMTS) 2025
The precision machining industry’s premier event returns to Cleveland, OH, April 1-3.
Read More





























.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)
















