The Knob Problem
The retention knob is an unmistakably critical component of the machining process. However, the tightening of the knob itself can lead to the toolholder not seating securely in the machine. You may be losing tool life to knob tightness without even knowing it.
Share





This video shows the toolholder deformation being measured for the high-torque and standard knob designs. For a similar demo video produced by J&M Machine, click on the link to this company under "Related Suppliers" at right.
Shops often give considerable care to just one end of a machining center’s toolholder—the end that holds the tool. On a tapered toolholder, the opposite end receives a retention knob. This knob is the near-invisible linchpin of the machining center process. It is often underappreciated.
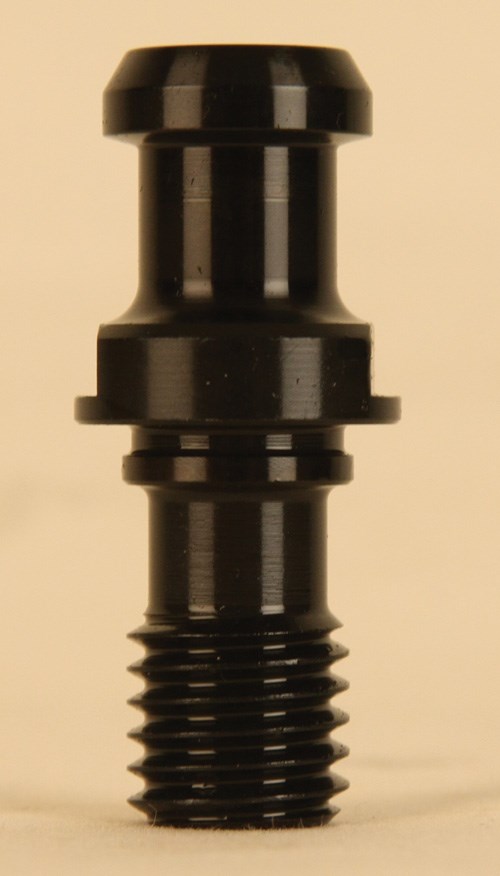
Still, the retention knob doesn’t ask for acclaim. It is a humble component performing a simple task. In a tapered holder such as the CAT or BT design, the knob screws into the holder to give the machining center’s drawbar an appropriate shape to grab. If the drawbar and retention knob do not work together effectively, then the toolholder might not fit properly into the machine’s spindle. Thus, this simple task is also critical, because how well the tool is secured is ultimately determined by how well the holder itself is secured.
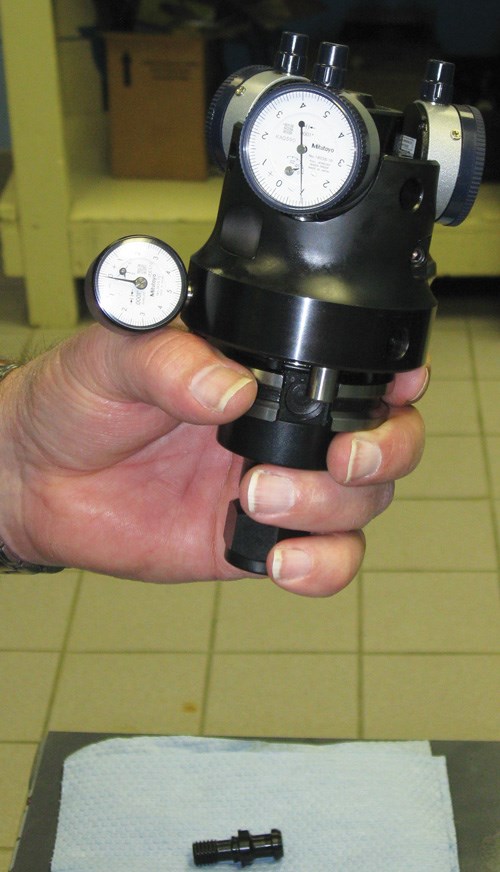
John Stoneback, president of J&M Machine in Fairport Harbor, Ohio, says he believes insecure holding of toolholders is far more typical of machining center processes than most shops realize. The problem lies in the potential effect of the knob itself on the holder. J&M makes retention knobs, and it recently began studying what happens to the toolholder when the knobs are tightened. The company developed a test fixture for this very purpose—measuring minute changes in a tapered toolholder’s shape.
The study found that across various makes and sizes of tapered toolholders, overtightening the retention knob by even a mild degree was enough to produce a bulge in the narrow end of the holder.
In fact, Mr. Stoneback says that in some cases just tightening the knob, not overtightening, was enough. The company has measured the effect in cases where just 10 to 15 foot-pounds of torque was applied.
As a result, the toolholder loses the shape that matches the cone of the spindle. This means the toolholder doesn’t fit the spindle precisely, leaving it free to move like a clapper in a bell.
This bell can’t be heard, but the effect of the movement can be seen. Mr. Stoneback has seen it himself. He says the mis-fitting of the toolholder explains a common wear pattern on toolholder tapers—one he has routinely seen on holders throughout his shop. The first photo above shows one of these holders. As it illustrates, toolholder tapers often show wear at the narrow end plus wear near the mouth. If the taper has black oxide coating, the region between these wear areas remains black. That’s because this part of the toolholder remains untouched, Mr. Stoneback says. On the distorted toolholder, this part of the taper never quite makes direct contact with the inside of the spindle.
Potential Impact
What this might mean for the stability at the tool tip and the life of the cutting tool are not hard to imagine. Carbide cutting edges are brittle when experiencing impacts other than those in the cutting direction. Where play exists between the toolholder and spindle taper, the resulting hammering of the tool is likely to speed the cutting edge toward failure.
This impact has been discovered in a big way in one particularly extreme application. J&M Machine developed an alternative retention knob design that produces less deformation of the holder when torqued to the same tightness as a standard knob. The knob has now been tested in a few shops, one of which performs aggressive slab milling of titanium. This shop had been accustomed to changing inserts two to three times per day. Once it switched to the new retention knobs, a single set of inserts lasted for a week without having to be changed.
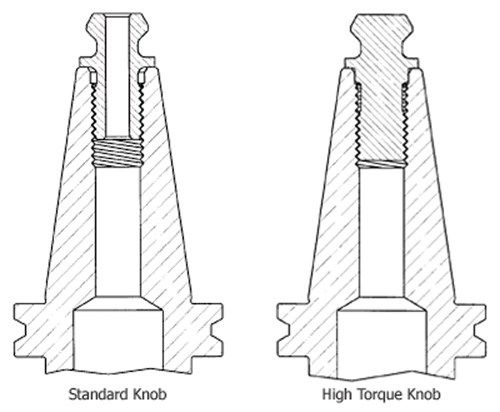
Illustrations above show the design difference of these “high-torque” or lower-deformation knobs. As the drawing shows, the knob has no threads to engage at the narrower part of the toolholder taper. The knob is also longer, reaching a little deeper into the holder’s threaded bore. As a result, all thread engagement occurs in a region of the toolholder where the diameter is large and where there is correspondingly more material to resist deformation. Where torque of 40 foot-pounds with a standard knob might deform a holder by three to five times the grind limit of 0.000080 inch, says Mr. Stoneback, the same torque with the high-torque knob deforms the holder by one times this limit.
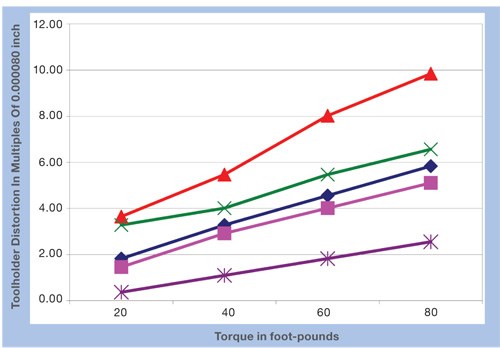
The use of the test fixture that the company developed can let a shop measure its own toolholders with and without tightened knobs to diagnose its own toolholder deformation. Video shows this measurement being done. (See "Editor Picks" above.) J&M Machine’s measurements revealed that holder deformation varies widely among different brands of both holders and knobs. The graph above illustrates the variation. This graph shows different knobs in the same holders, but similar variation was found when the same standard knob was used in different holders.
On this graph, the most extreme deformation seen is about 0.0008 inch. When the toolholder is in use, this discrepancy increases by a factor of 3.4 as the diameter of the taper increases toward the mouth of the spindle—to about 0.0027 inch. That’s a lot. Fortunately though, in a way, it’s also not that much.
The Good News
Mr. Stoneback points out that it’s likely that a shop’s toolholders are all still usable. His shop’s were.
The extent of deformation measured was all in the elastic range, meaning the holder recovers its shape each time the retention knob is removed.
The extent of impacts within the spindle resulting from a loose fit also typically will not have been enough to damage the holder. Any noticeable wear is likely to be visible only because the taper has a black oxide finish. The underlying form of the holder is still good.
All of this means that the shop that can get its retention knob tightening under control can probably begin using its current holders within a process that holds this tooling much more securely. As the shop begins to fully make use of its tapered holders, says Mr. Stoneback, the previously untouched part of the taper won’t go to waste after all.
Related Content
Workholding Fixtures Save Over 4,500 Hours of Labor Annually
All World Machinery Supply designs each fixture to minimize the number of operations, resulting in reduced handling and idle spindle time.
Read MoreThe Power of Practical Demonstrations and Projects
Practical work has served Bridgerland Technical College both in preparing its current students for manufacturing jobs and in appealing to new generations of potential machinists.
Read MoreFinding the Right Tools for a Turning Shop
Xcelicut is a startup shop that has grown thanks to the right machines, cutting tools, grants and other resources.
Read MoreCan Connecting ERP to Machine Tool Monitoring Address the Workforce Challenge?
It can if RFID tags are added. Here is how this startup sees a local Internet of Things aiding CNC machine shops.
Read MoreRead Next
Registration Now Open for the Precision Machining Technology Show (PMTS) 2025
The precision machining industry’s premier event returns to Cleveland, OH, April 1-3.
Read MoreSetting Up the Building Blocks for a Digital Factory
Woodward Inc. spent over a year developing an API to connect machines to its digital factory. Caron Engineering’s MiConnect has cut most of this process while also granting the shop greater access to machine information.
Read More5 Rules of Thumb for Buying CNC Machine Tools
Use these tips to carefully plan your machine tool purchases and to avoid regretting your decision later.
Read More