Spark Control Pushes Wire EDM Boundaries
Precisely controlling and monitoring each individual spark enables this wire EDM machine to cut hardened, high-temperature alloys with high precision.
Share








ECi Software Solutions, Inc.
Featured Content
View More
Takumi USA
Featured Content
View More
Hwacheon Machinery America, Inc.
Featured Content
View MoreWhile not traditionally considered a viable option for machining high-temperature alloys, wire EDM is getting a second look from shops struggling with titanium, Inconel and other such problematic but increasingly popular materials. In fact, the latest wire EDM machines can not only effectively cut these hardened, often proprietary metal blends, but can do so with unprecedented levels of speed and precision.
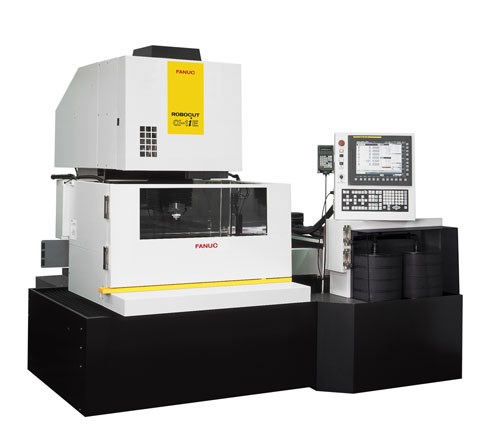
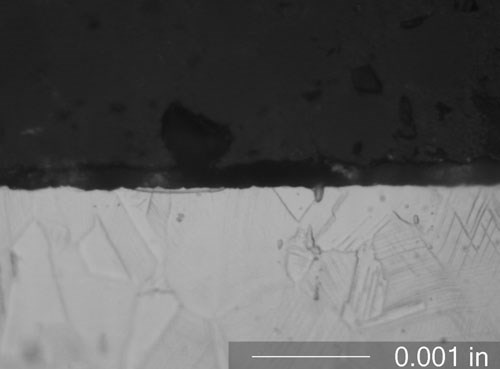
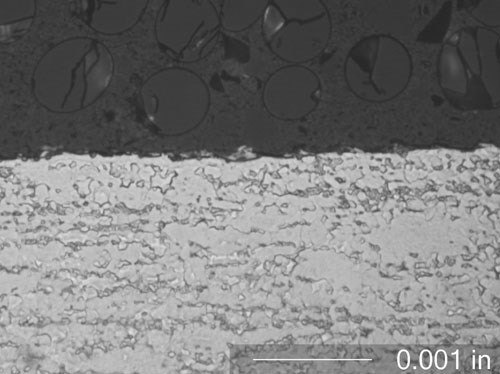
Fanuc’s new Robocut iE series is representative of this next generation of wire EDM technology. Available from Methods Machine Tools, these machines are said to achieve geometric accuracy to less than 0.0001 inch. They also virtually eliminate the undesirable effects of recast layers and other surface finish imperfections that once limited wire EDM’s application in high-temperature alloys, the company says.
In large part, the machine accomplishes these benefits by both controlling and monitoring the tens of thousands of tiny sparks discharged each second to remove material from the workpiece, says Steve Bond, national sales manager at Methods Machine Tools. Spark control is accomplished primarily via a new digital power supply with an embedded microprocessor. Through complex calculations, the power supply adjusts each spark’s energy, duration and other properties. The goal is to ensure effective cutting without generating enough heat to cause some of the workpiece material to re-adhere to the part surface as a recast layer. The spark properties required to achieve that end differ from alloy to alloy, so the power supply must be “tuned” according to the particular material. Mr. Bond explains that this is accomplished by reducing the power on the wire (voltage and amperage) on the final two skim cuts using Fanuc’s pulse mode 15.
A redesigned lower arm facilitates spark control by preventing stray electrical energy throughout the machine enclosure from adding heat that can contribute to recast layer formation. During finishing passes, the lower arm power feed contact moves away from the wire. Meanwhile, a specially designed diamond guide keeps the wire in place. This effectively isolates the lower head from the rest of the machine tool to keep energy out of the rest of the enclosure and concentrated where it belongs: in the wire at the point of the cut. “The less mechanical parts you’ve got up against the wire that can take power away from it, the better off you are,” Mr. Bond explains.
He emphasizes that despite these advances, EDM is a thermal process, so it will always create some recast. Nonetheless, the Robocut iE machines outclass what past wire EDMs have achieved in machining high-temperature alloys, he says. “You have your naysayers, but it’s getting attention from people who say they’ve never seen these kinds of results before off any other EDM. One could argue that you can never totally get rid of recast, and that’s true, but these machines are still producing aerospace and medical parts in titanium, Inconel, Waspalloy and other materials that are more than acceptable.”
While controlling spark properties prevents recast and other imperfections, monitoring the spark and adjusting cutting parameters accordingly improves speed, accuracy and surface finish, Mr. Bond says. For that, the iE series incorporates Ai Pulse Control, a feature that determines whether each discharge pulse has effectively contributed to material removal. Then, it adjusts the feed rate according to the number of effective discharge pulses. This keeps the energy density and the discharge gap uniform to enable smoother cutting at higher speeds, significantly reducing witness lines and other surface imperfections. “This is a form of adaptive control, but it’s the next generation,” Mr. Bond explains. “Before, we could only monitor the total voltage gap, but now we’re actually monitoring each spark. That is much more accurate and much more responsive to what is going on in the cut.”
Related Content
Where Micro-Laser Machining Is the Focus
A company that was once a consulting firm has become a successful micro-laser machine shop producing complex parts and features that most traditional CNC shops cannot machine.
Read MoreThe Future of High Feed Milling in Modern Manufacturing
Achieve higher metal removal rates and enhanced predictability with ISCAR’s advanced high-feed milling tools — optimized for today’s competitive global market.
Read MoreHigh RPM Spindles: 5 Advantages for 5-axis CNC Machines
Explore five crucial ways equipping 5-axis CNC machines with Air Turbine Spindles® can achieve the speeds necessary to overcome manufacturing challenges.
Read More5 Tips for Running a Profitable Aerospace Shop
Aerospace machining is a demanding and competitive sector of manufacturing, but this shop demonstrates five ways to find aerospace success.
Read MoreRead Next
5 Rules of Thumb for Buying CNC Machine Tools
Use these tips to carefully plan your machine tool purchases and to avoid regretting your decision later.
Read MoreBuilding Out a Foundation for Student Machinists
Autodesk and Haas have teamed up to produce an introductory course for students that covers the basics of CAD, CAM and CNC while providing them with a portfolio part.
Read MoreRegistration Now Open for the Precision Machining Technology Show (PMTS) 2025
The precision machining industry’s premier event returns to Cleveland, OH, April 1-3.
Read More









.png;maxWidth=150)
























.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)














