Saving Time and Money on the Shop Floor with AM
The ways additive manufacturing is presented sometimes miss the most practical and valuable ways it can be used.
Share






.png;maxWidth=45)
DMG MORI - Cincinnati
Featured Content
View More
ECi Software Solutions, Inc.
Featured Content
View More



Additive manufacturing (AM) hardware and software providers tout the design and material freedom of AM. They do this so much that I believe most companies — and the engineers and designers working for them — think of AM as a design tool, not a manufacturing solution. In fact, look at the distribution channels for most AM hardware systems. They are CAD vendors and resellers who market to engineers and designers, not machining experts that cater to job shops or manufacturing and process engineers.
While I have touched on this in previous columns (see “Does Manufacturing Need Additive?” and “Is Additive Freeing Designers or Aiding Manufacturing?”), the point became painfully obvious to me a few months ago when I was preparing my talk for the 3D Printing Workshop for Job Shops at the International Manufacturing Technology Show (IMTS) in Chicago in September 2022. This new workshop was targeted specifically at manufacturing professionals and machining experts looking to find ways to improve operations on the shop floor rather than design the complex, organic-shaped, lightweight structures being heralded by others elsewhere in the AM exhibit hall.
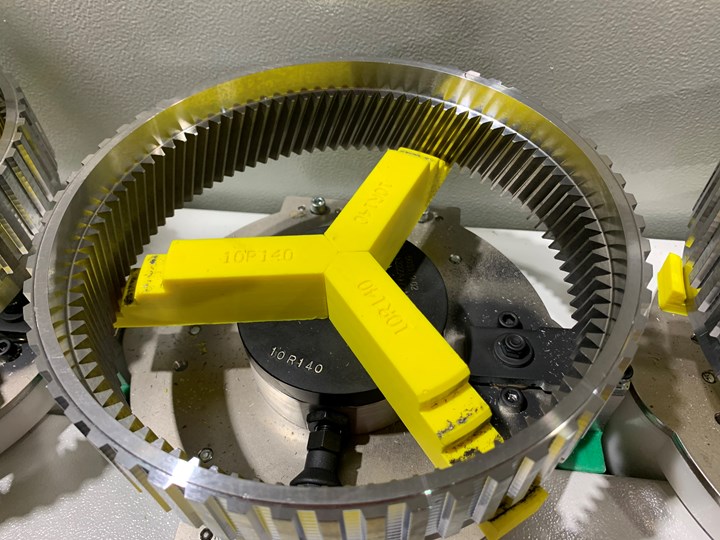
A broaching operation for transmission ring gears at Ford was damaging the steel rings because of the specialized metal fixtures that were formerly used to hold the rings in place. 3D printing the fixtures out of PETG solved the problem, putting a $1 million problem to rest. Photo Credit: Sharonville Transmission Plant
As I prepared my presentation for IMTS, I realized that none of the examples or case studies that I usually discuss were relevant to the anticipated audience. In fact, the whole point of using AM on the shop floor is different from those using it for product design and development. Granted, consolidating a multi-part assembly with AM may save some time and labor, but topology optimization, customization, conformal cooling, lattice structures, functionally graded materials and the like have little to no meaning to manufacturing professionals and machining experts using 3D printing to support the work of a job shop. It is the engineers and designers that care about that stuff because it helps them meet product requirements in new and better ways.
The requirements that manufacturers need to meet are related to cost and lead time, not lightweighting a component to improve fuel economy of a vehicle, for example. As a result, the uses and applications for AM are different on the shop floor than how AM is being sold to most industries.
So how can AM help save cost and time on the shop floor? Examples abound; they just aren’t often showcased in stories about AM’s successes, and they certainly don’t go viral on social media. As a result, we miss out on the practical applications and uses of AM that can actually save time and money on the shop floor. For example, AM technology can be used to create any or all of the following, often at less time and cost:
- Jigs and fixtures
- Tooling and workholding
- Assembly/disassembly jigs
- Custom assembly tools
- Alignment tools and ergonomic grips
- Soft jaws and custom chucks
- Welding fixtures and bonding jigs
- Drill guides
- Go/No-Go gauges
- Inspection fixtures
- Custom masking/marking/labeling tools
- Surrogate parts (for pre-production validation)
- Poka-yoke (to avoid operator errors and mistakes)
- Replacement parts (for older mills, lathes and legacy manufacturing equipment)
As for quantifying the cost and time savings, three examples I used in my talk are:
- Volvo Trucks used material extrusion AM technology to reduce turnaround time on tooling for their assembly lines by 94% (2 days versus 36 days); it also saved significantly on the cost of the tooling.
- Google Advanced Technology and Projects used vat photopolymerization AM technology to produce surrogate parts that reduced turnaround time by 85% and saved over $100,000 on an over-molded wearable device that was being produced.
- Dixon Valve used material extrusion AM to make custom grippers that saved 97% of the cost ($9.06 versus $290.35) while reducing turnaround time by 87%.
Finally, for those that want to learn more, Additive Manufacturing Media maintains a list of 10 examples of 3D printed tooling while AM hardware providers like FormLabs, Stratasys and MarkForged, along with AM service providers like Javelin, GSC and PrintYourMind, provide examples that will inspire creative ways to use AM to save time and money on the shop floor.
Related Content
Chuck Jaws Achieve 77% Weight Reduction Through 3D Printing
Alpha Precision Group (APG) has developed an innovative workholding design for faster spindle speeds through sinter-based additive manufacturing.
Read MoreDesigning a 3D Printed Part with Machining in Mind
Designing extra stock and mounting features into a 3D printed part can aid in machining processes downstream.
Read MoreThe Cool Parts Showcase Seeks Innovative 3D Printed Parts
Do you solve problems with 3D printing? Enter your 3D printed parts in this contest from The Cool Parts Show.
Read MoreDigital Thread Enables First-Time-Right 3D Printing
Connecting all stages of manufacturing, from design to postprocessing, helps break down barriers to industrializing additive manufacturing.
Read MoreRead Next
Building Out a Foundation for Student Machinists
Autodesk and Haas have teamed up to produce an introductory course for students that covers the basics of CAD, CAM and CNC while providing them with a portfolio part.
Read MoreRegistration Now Open for the Precision Machining Technology Show (PMTS) 2025
The precision machining industry’s premier event returns to Cleveland, OH, April 1-3.
Read More5 Rules of Thumb for Buying CNC Machine Tools
Use these tips to carefully plan your machine tool purchases and to avoid regretting your decision later.
Read More


































.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)