Dressing Well: The Key To Grinding Quality
Because the nature of the interface between wheel and workpiece largely defines grinding quality and efficiency, it's essential to maintain optimum conditions within this critical zone. Therein lies the key to sustaining grinding as a competitive process.
Share





Advances in high speed milling and hard turning have presented some stiff competition for grinding processes. At the same time, the increasing complexity of part designs demands significantly greater flexibility in grinding capabilities. Faced with these challenges, the future viability of many types of grinding operations depends on the continuous optimization of all process parameters. Because the nature of the interface between wheel and workpiece largely defines grinding quality and efficiency, it’s essential to maintain optimum conditions within this critical zone. Therein lies the key to sustaining grinding as a competitive process.
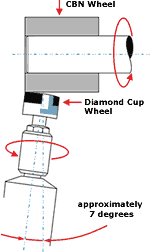
Using cubic boron nitride (CBN) media to grind steels of 60 HRc or greater is one important way that machine shops have optimized their processes. The principal benefits of CBN tools are longer dressing intervals and reduced idle times. These enable faster, more accurate and economical production of close-tolerance parts across a wide range of machining speeds. In certain applications, CBN wheels can reduce machining times by 50 to 66 percent compared to conventional abrasives.
But choosing a particular grinding medium represents only part of the overall productivity picture. Maintaining an accurate orientation between the grinding wheel and workpiece is fundamental to efficient, high-quality production. Additionally, the wheel’s surface must be maintained in the proper condition. These critical functions are accomplished via profiling and dressing. The relative aggressiveness of grinding tools and the resultant surface finishes depend on the type and quality of dressing procedures. For example, the surface profile of a roughly dressed grinding wheel incorporates relatively high peak-to-valley heights. This makes the wheel sharp and aggressive, but it also transfers the wheel’s surface roughness onto the workpiece. This produces a lower-quality ground surface than that produced by a finely dressed wheel.
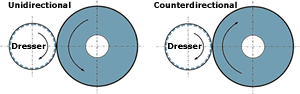
Rotary dressing and profiling depend to a significant extent on the rigidity of a grinding machine’s dressing spindle. The relationship of motion between the dressing and grinding tools is also a key factor. “The direction of rotation and the relative circumferential speed between the grinding wheel and the dressing tool change the shape of the grinding wheel,” says Thomas Frisch, project leader of R&D for spindle supplier Fischer AG (U.S. headquarters: Fischer USA Spindle Technologies Inc., New Brighton, Minnesota). “This is decisive for the wheel’s abrading performance and the surface finish of the workpiece.”
Unidirectional dressing occurs when the dressing tool rotates in the same direction as the grinding wheel (whether the two axes of rotation are parallel or perpendicular). This configuration transfers a higher degree of surface roughness to the grinding wheel for applications that demand faster material removal rates. When the surface quality of the workpiece is the principal criterion, however, a counter directional motion is necessary to produce a finely dressed grinding wheel.
A rotary dressing unit incorporates a motorized spindle with either a diamond roll dresser or a diamond dressing-wheel. To achieve precise control of dressing routines, Fischer has developed the RotoDress Motor Dressing spindles, types AES-72 and MZ-50. Incorporating frequency converters, these spindles may be operated at variable speeds up to 30,000 rpm. The spindles are powered by asynchronous, reversible motors.
Another important aspect of process optimization is matching the performance characteristics of the grinding spindle to those of the rotary dressing spindle. Similarly, diamond dressing tools should be chosen for compatibility with specific types of grinding wheels. This underlines the importance of using a supplier that offers a comprehensive range of grinding products.
Related Content
6 Machine Shop Essentials to Stay Competitive
If you want to streamline production and be competitive in the industry, you will need far more than a standard three-axis CNC mill or two-axis CNC lathe and a few measuring tools.
Read MoreWhat are Harmonics in Milling?
Milling-force harmonics always exist. Understanding the source of milling harmonics and their relationship to vibration can help improve parameter selection.
Read MoreHow to Optimize Operator Efficiency on Any Shop Floor
Striking the perfect balance of person to machine is unique to each shop and can depend on a number of factors, including the type of work a shop undertakes, the available equipment, staffing levels, scheduling and more.
Read More4 Steps to a Cobot Culture: How Thyssenkrupp Bilstein Has Answered Staffing Shortages With Economical Automation
Safe, economical automation using collaborative robots can transform a manufacturing facility and overcome staffing shortfalls, but it takes additional investment and a systemized approach to automation in order to realize this change.
Read MoreRead Next
Setting Up the Building Blocks for a Digital Factory
Woodward Inc. spent over a year developing an API to connect machines to its digital factory. Caron Engineering’s MiConnect has cut most of this process while also granting the shop greater access to machine information.
Read MoreRegistration Now Open for the Precision Machining Technology Show (PMTS) 2025
The precision machining industry’s premier event returns to Cleveland, OH, April 1-3.
Read More5 Rules of Thumb for Buying CNC Machine Tools
Use these tips to carefully plan your machine tool purchases and to avoid regretting your decision later.
Read More