The most notable innovation in Mitsubishi EDM’s new MV series of wire EDMs is the use of axis drive units based on linear shaft motors (LSMs). These motors replace conventional ballscrew-based drive units and are an alternative to flat-plate linear motors. The MV series of wire units represents a general upgrade to the company’s various FA, BA and MD+Pro II models. In addition to LSM technology, the MV series features a redesigned automatic wire rethreading system, an enhanced power supply and high speed communication in the servo system, among other advances.
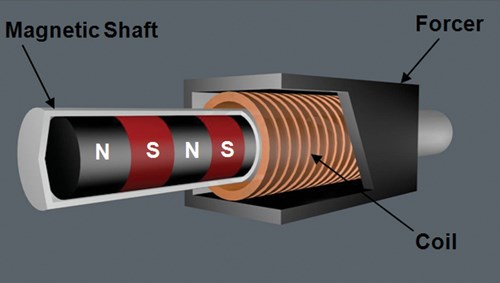
LSMs are based on a design concept that may be unfamiliar to many end-users. As explained by the company, the distinguishing feature of this type of linear motor is the shaft—a cylindrical component in which high-power permanent magnets are embedded. This shaft fits inside, but it does not contact, a forcer unit that surrounds it with an electromagnetic coil. When energized, the coil creates a magnetic flux that encircles the shaft and interacts with the magnets inside. This propels the forcer along the shaft.
Until now, most linear motors applied to machine tools (including EDM units) have been the flat-plate type. Typically, this type consists of two plates that face each other, with iron-core magnetic coils on the primary side and a strip of magnets on the secondary side. The plates never touch, but they must be mounted precisely to maintain an optimal gap between them. As the top plate travels over the magnets, they create magnetic flux. However, this flat-plate design limits the flux to only half of its potential because only the top part of the magnets is utilized.
In contrast, the shaft and forcer unit of an LSM are configured much like the screw and nut on a conventional ballscrew drive unit. This enables machine designers to utilize an LSM in place of the ballscrew by making relatively minor modifications to the base and table of the machine tool.
According to Mitsubishi EDM, the LSM has a number of advantages compared to flat-plate linear motors. For one, compared to flat-plate-type motors, the coreless design of LSM drives creates little heat in operation. On flat-plate motors, coils wrapped around iron cores heat up rapidly when energized. In addition, magnetic flux induced between the plates can be utilized only where the front surfaces are directly facing each other. Magnetic forces exerted elsewhere, such as at surfaces on the back side of the plate, represent lost efficiency and dissipate as heat energy. These sources of heat must be counteracted with multiple internal liquid cooling systems, adding to complexity of machine design. In contrast, an LSM requires only the forcer to use liquid cooling to remove what little heat is generated.
Another favorable characteristic of LSM’s non-core technology is the absence of the cogging effect inherent in plate-type linear motors. Depending on the size and spacing of the coil-wound iron cores on one side and the permanent magnets on other side, the thrust forces created by the magnetic flux varies in wave-like intensity, magnet to magnet. This causes the movable plate to lurch slightly as it is tugged by the uneven forces, especially when decelerating. This effect reduces position accuracy and hinders smooth transport of axis components. On a coreless LSM, the tight, uniform windings of the coil in the forcer create consistent thrust forces that are distributed evenly around for circumference of the shaft so cogging does not occur. Moreover, the gap between the shaft and the forcer is less critical, and it is less likely to be contaminated by particulate matter.
Compared to conventional ballscrew drives, the non-contact design of the LSM creates no friction, causes no wear, requires no lubrication, does not expand from heat, and produces no noise. An LSM also has no pitch error or backlash and requires no adjustments over time to compensate for wear of mechanical components.
The MV series also has a new automatic wire rethreader that anneals and straightens a longer section of electrode wire to enable rethreading at the breakpoint up to 8-inches thick even while fully submerged. Power supply enhancements include anti-electrolysis settings that are effective during high-speed cutting, settings for finishes that are 30-percent finer than previous models at higher speeds, and an operator interface with a simplified menu design. In addition, a Digital Matrix Sensor works with the power supply to shape the pulse to reduce electrode wear. Thus, wire speed can be reduced by as much as 60 percent without sacrificing feature straightness or finish. Also notable is the high-response fiber optical servo system that features communication speed four times faster than the system used previously, so machine position and spark discharge status can be monitored more accurately for nano-level precision.
Learn more about MC Machinery Systems.