Share







ECi Software Solutions, Inc.
Featured Content
View More


Takumi USA
Featured Content
View More.png;maxWidth=45)
DMG MORI - Cincinnati
Featured Content
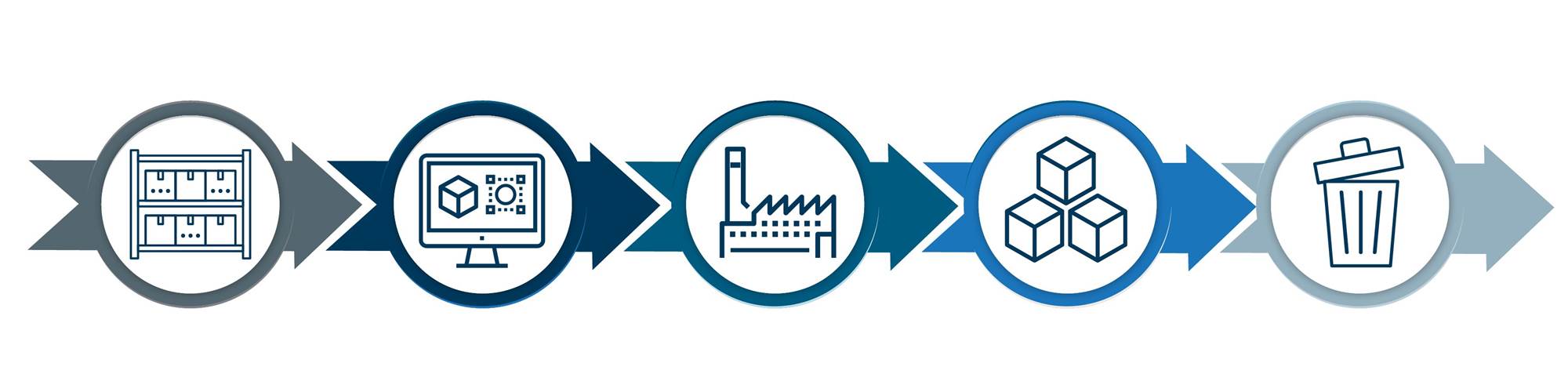
View MoreSince the Industrial Revolution at least, our cycles of production and consumption have become quite linear. Resources are extracted from the earth in the form of ore, petroleum and other raw substances, transformed into materials that are then manufactured into products, sold to consumers, and from there are likely to be discarded at the end of their lifecycles.
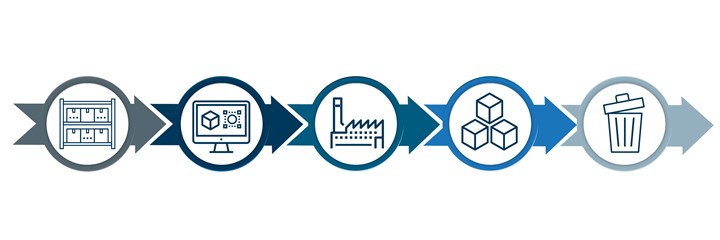
The linear economy has a clear beginning and end, with materials transforming into products and being discarded at the end of their lifespans.
Over at Modern Machine Shop’s sister publication, Additive Manufacturing, we’ve been devoting some of our coverage this year to a different model, the circular economy. This concept closes the loop of the linear economy, stipulating that used products and materials should not be discarded, but fed back into the cycle. (For a much more detailed explanation, see this page and other resources from the Ellen MacArthur Foundation.)
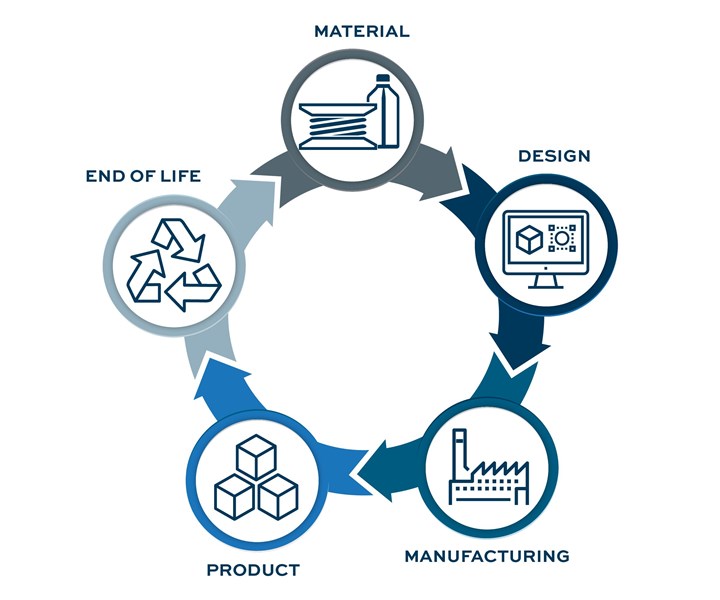
The circular economy closes the loop, feeding used products, scrap, and other materials back into the cycle of production.
The goal in doing so? To reach a point of sustainability, in which the cycle can carry on. The linear economy isn’t sustainable in this way; once the raw materials it depends on are gone, it cannot continue as it once did.
Because circularity hinges on what happens at the end of the product lifecycle, it might seem that recycling is the solution, that if more recycling facilities existed and consumers became more diligent about returning used products, this would solve the problem. But in fact the adage to “Reduce, Reuse, Recycle” is a hierarchy: Recycling is actually the third choice option, after reducing material usage in the first place and seeking reuse options.
With that in mind, circularity actually begins much sooner in the production process. It starts with the materials and the design of the product; careful choices in these early stages can result in products that can be more easily reused, refurbished or recycled, if necessary.

The post-redesign Steelcase Think chair contains fewer parts and materials than the original, is easier to disassemble, and is up to 95% recyclable by weight. Photo Credit: Steelcase
Take for example an office chair, with a padded seat, arm rests, casters and height adjustment capability. A chair like this could contain hundreds of components and fasteners made from dozens of different materials including metals, plastics, foams and fabrics. This chair would time-consuming to assemble in the first place, but also tedious to disassemble into its respective parts for repair or recycling. But if the manufacturer were to design a simpler assembly, using fewer, more renewable materials, the chair could be more easily maintained, reused or recycled as well as simpler to make in the first place.
Furniture manufacturer Steelcase actually did a redesign like this on its popular Think chair. The company reduced and reassessed the materials used, for instance swapping a virgin polyamide plastic for one made from recycled preconsumer plastic. Up to 95% of the product by weight is now itself recyclable. Components were consolidated; the entire back of the redesigned chair is just three parts. And, the chair can now be disassembled in five minutes using basic hand tools.
Could the part and materials count be reduced even further? Almost certainly, with the use of additive manufacturing (AM). Steelcase is in fact already using 3D-printed components in a different product; its SILQ chair features armrests that were previously assembled from three different parts, and are now 3D printed as a single piece.
As the example above illustrates, circularity and sustainability can be pursued with conventional manufacturing methods just by reconsidering the design and materials used. But these principles can potentially be advanced further with the added advantage of additive manufacturing, which can allow for lightweight designs that use less material, consolidated assemblies, new material options, and more. If applied broadly to cars, planes, even houses, the impact could be astronomical.
If you’d like to learn more about the circular economy and how it can advance with 3D printing, here are some additional resources from Additive Manufacturing:
- What Is the Circular Economy, and How Can 3D Printing Help? (the first in a video series)
- Additive Manufacturing Will Aid and Accelerate the Circular Economy (a longform piece on how 3D printing can support each stage of the circular economy)
- Additive Manufacturing and Sustainability Go Together — Here Is Why (the editor’s column for our July/August sustainability issue, including links to the stories)
Related Content
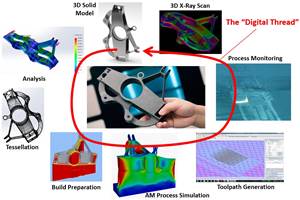
Digital Transparency in Machining Key to Multi-Site Additive Manufacturing
Cumberland Additive’s CNC programmer in Pennsylvania spends most of his time writing programs for machine tools in Texas.
Read MoreThe Cool Parts Showcase Seeks Innovative 3D Printed Parts
Do you solve problems with 3D printing? Enter your 3D printed parts in this contest from The Cool Parts Show.
Read MoreA Fond Farewell to My Additive Friends
In his final “Additive Insights” column, Tim Simpson reflects on how additive manufacturing has progressed in the last six years. Standards and software are two examples.
Read MoreGo Digital: How to Succeed in the Fourth Industrial Revolution With Additive Manufacturing
The digitalization of manufacturing is set to transform production and global supply chains as we know them, and additive manufacturing has been leading the way in many industries.
Read MoreRead Next
Additive Manufacturing Belongs in a Machine Shop
A fourth-generation family machine shop integrates metal additive manufacturing as another production operation.
Read More5 Rules of Thumb for Buying CNC Machine Tools
Use these tips to carefully plan your machine tool purchases and to avoid regretting your decision later.
Read MoreBuilding Out a Foundation for Student Machinists
Autodesk and Haas have teamed up to produce an introductory course for students that covers the basics of CAD, CAM and CNC while providing them with a portfolio part.
Read More
.jpg;width=70;height=70;mode=crop)






























.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)





.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)