“Swiss Automatic” Grinder…Made in Jersey
This microgrinding machine uses a hydrostatic bearing akin to the guide bushing on a sliding-headstock, Swiss-type lathe to grind really long, really skinny parts.
Share





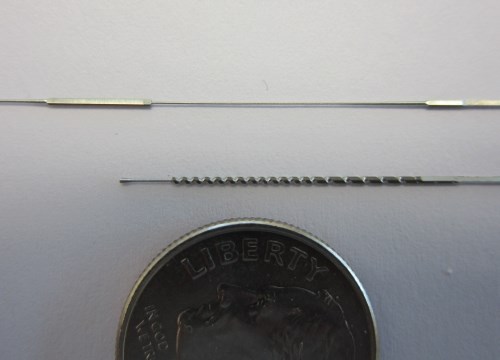
The CAM.2 microgrinding machine from Glebar uses a hydrostatic bushing to offer support very near the area of contact between the part and the grinding wheel. There’s pretty much no limit to the length of wire to be ground, as shown in these demonstration parts with tiny ground flats, tapers, threads and so on.
Glebar, a New Jersey manufacturer of OD grinders, plunge grinders and other types of grinders, developed an interesting technology for grinding long, small-diameter parts. We’re talking workpiece stock as small as 0.005 inch in diameter and a minimum grinding diameter of 0.0005 inch for applications such as medical guidewires that can range to 16-feet long.
The way it does that is by applying a concept that’s similar to a sliding-headstock, Swiss-type lathe and its signature guide bushing. Learn more.
Related Content
-
The Future of High Feed Milling in Modern Manufacturing
Achieve higher metal removal rates and enhanced predictability with ISCAR’s advanced high-feed milling tools — optimized for today’s competitive global market.
-
How to Determine the Currently Active Work Offset Number
Determining the currently active work offset number is practical when the program zero point is changing between workpieces in a production run.
-
How to Mitigate Chatter to Boost Machining Rates
There are usually better solutions to chatter than just reducing the feed rate. Through vibration analysis, the chatter problem can be solved, enabling much higher metal removal rates, better quality and longer tool life.





















