Share





ECi Software Solutions, Inc.
Featured Content
View More


Hwacheon Machinery America, Inc.
Featured Content
View More
Takumi USA
Featured Content
View MoreIn a production-grinding operation, waviness on the part surface is a potential clue that the machine or process has developed a vibration problem. The effect might be seen in inspection, or if there is a lapping or polishing step, more time might be spent during that step removing the waves. According to grinding wheel manufacturer Norton Saint-Gobain Abrasives, this is the point at which shops almost always attempt to solve the vibration problem by making some simple change to the process, which is a pretty good approach.
Indeed, those waves on the surface, often called chatter, could indicate the appropriate fix. (Others use “chatter” to refer to regenerative waviness. The use here is not that specific.) On a part machined on a surface grinder, for example, vibration frequency (cycles per minute) is equal to the work speed (inches per minute) divided by the distance between two consecutive chatter marks (inch). Find the vibration frequency using this relationship, and if it matches the rotation speed of the grinding spindle, then this indicates that the grinding wheel, wheel flanges or the grinding spindle itself is a likely culprit. Change the wheel, tighten the flange bolts, or perhaps just change speed, and that much might be enough to cure or control the vibration problem.
But in other cases—some involving other parts of the machine, some involving the natural frequency of the system—a simple fix is not enough to sufficiently address the problem. In these cases, the very best response is to have the machine serviced, repairing whatever failing machine element is allowing vibration to affect the workpiece. Service, however, takes time, and it means taking the machine out of production. For shops that need to keep going, if only for the short term, researchers have proven out a process for overcoming vibration’s effects without compromising productivity and without stopping the machine for service.
What follows is derived from a paper about a technique called “contact-length filtering” written by Saint-Gobain corporate applications engineers John Hagan and Mark Martin. By reducing the work feed rate while increasing the depth of cut, the effects of severe vibration can be eliminated without any net effect on overall productivity.
Large Wheel-to-Work Ratio
The aim of contact-length filtering is to get the wheel-to-work contact length very large relative to the wavelength of the surface affected by vibration. When the former is high enough relative to the latter, the wheel effectively removes vibration-related peaks from the workpiece, smoothing out the surface even though vibration is still occurring. When the depth of cut is increased by the same multiple that feed rate is decreased, material removal rate (and therefore productivity) can remain the same.
The depth of cut controls contact length. Obviously, the contact length’s increase needs to avoid unfavorable effects such as material burn, workpiece deflection and so on. Usually this is accomplished by increasing the wheel’s depth of cut to a level that is heavy compared to standard cutting conditions, but still avoids these ill effects.
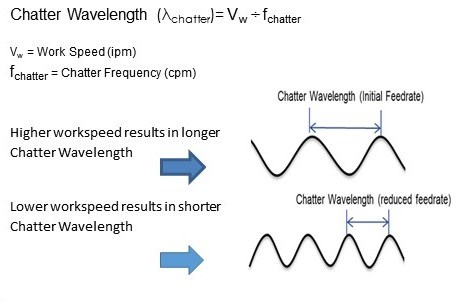
Meanwhile, the feed rate (or work speed) controls the wavelength of the vibration marks in the part. A slower speed shortens the wavelength.
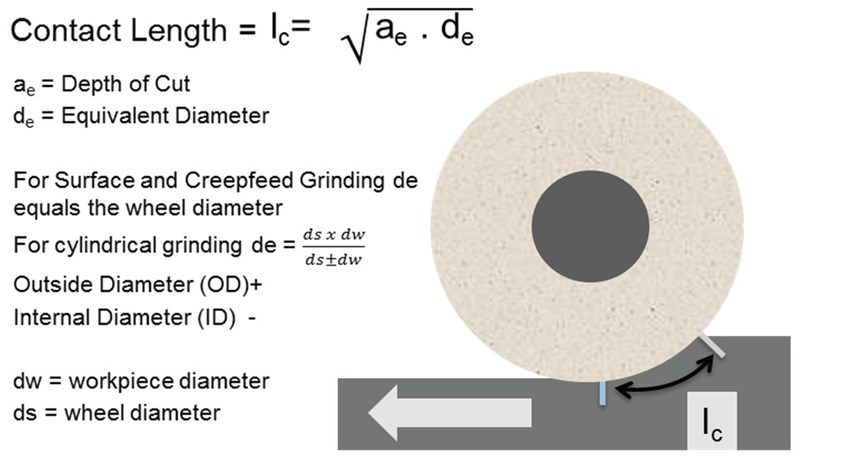
Contact-length filtering begins to achieve a smooth surface when double the wheel-to-work contact length surpasses the wavelength of the chatter, or surface waviness. In other words, the condition required for chatter amplitude reduction is….
2 x Contact Length (lc) ≥ Chatter Wavelength (λchatter)
Where…
- Figure 1 defines the Contact Length (lc), and
- Figure 2 defines the Chatter Wavelength (λchatter)
The technique won’t always work, the researchers say. It won’t be possible in every process to get the vibration wavelength low enough or the contact length high enough. In these cases, the only remaining solution is the one that needs to be performed anyway, namely, take the time to identify and correct the vibration’s underlying cause. What follows is a case in which contact-length filtering was effective for machining a smooth surface in spite of extreme vibration.
Case Study
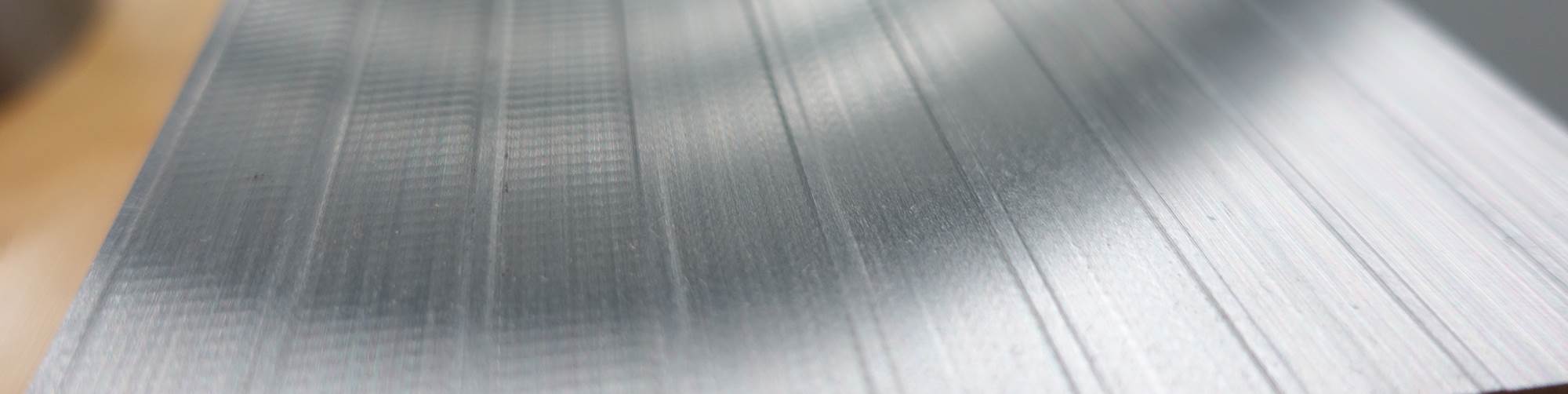
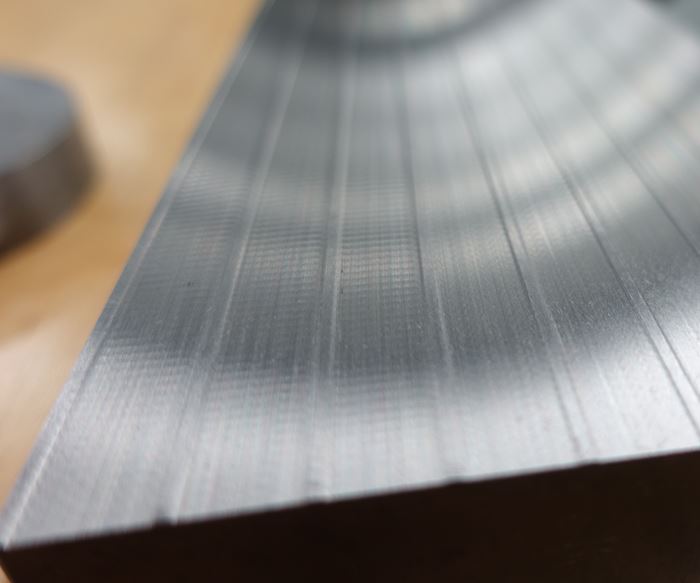
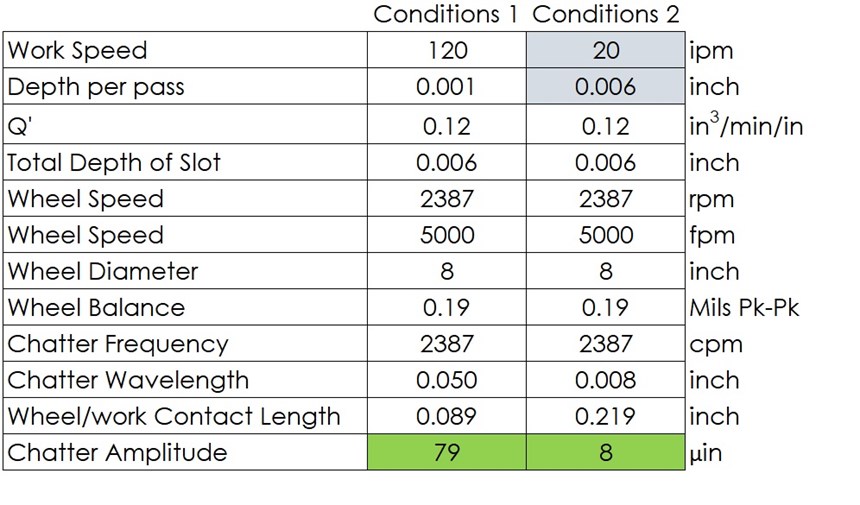
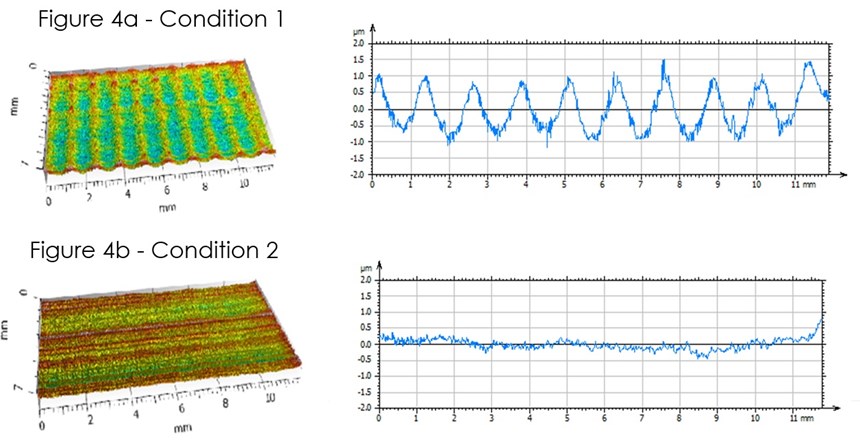
This study was designed to show the effect contact-length filtering can have on reducing chatter due to vibration. The grinding test was performed at the Saint-Gobain Higgins Grinding Technology Center near Boston, Massachusetts. The test machine was an Elb creep-feed/surface grinder. The operation was slot grinding using an 8-inch-diameter, ½-inch-wide conventional abrasive wheel. The material ground was 4340 hardened steel. The wheel was intentionally thrown out of balance by adding weights to one side of the wheel hub. The vibration due to wheel unbalance was measured at 0.00019-inch displacement. The first test involved grinding three slots at “Conditions 1,” as shown in Figure 3. The feed rate was 120 inches per minute, and depth of cut was 0.001 inch. Six passes were made for each slot to achieve a total depth of 0.006 inch. The material removal rate was 0.12 cubic inch per inch of wheel width. The effects observed on the workpiece at these conditions was significant, as seen in Figure 4a.
The second part of the test involved grinding three slots at “Conditions 2” shown in Figure 3. Here, the feed rate was reduced to 20 inches per minute, and the total depth was achieved in a single pass at a depth of cut of 0.006 inch. The wheel imbalance remained the same at 0.00019 inch. The material removal rate also remained the same. The vibration amplitude observed on the workpiece at these conditions was greatly reduced, as can be seen in Figure 4b. The vibration amplitude at the second set of conditions was measured at 8 microinches versus 79 microinches when grinding at first set of conditions.
Again, the imbalance remained the same. But grinding at conditions consistent with contact-length filtering produced a smooth surface despite the imbalance, without any reduction in productivity.
The technique has its limitations, the researchers stress. The case study represents an ideal scenario. It won’t be possible in every process to achieve the condition of twice the contact length being larger than the vibration wavelength, let alone without any loss to material removal rate. But in the right applications, this technique is potentially a powerful option. It is a way to keep going, and to continue realizing an acceptable surface through production grinding, until the right moment comes when the valuable machine can be taken offline for repair.
Related Content
6 Machine Shop Essentials to Stay Competitive
If you want to streamline production and be competitive in the industry, you will need far more than a standard three-axis CNC mill or two-axis CNC lathe and a few measuring tools.
Read MoreHow to Choose the Correct Measuring Tool for Any Application
There are many options to choose from when deciding on a dimensional measurement tool. Consider these application-based factors when selecting a measurement solution.
Read More4 Commonly Misapplied CNC Features
Misapplication of these important CNC features will result in wasted time, wasted or duplicated effort and/or wasted material.
Read More4 Steps to a Cobot Culture: How Thyssenkrupp Bilstein Has Answered Staffing Shortages With Economical Automation
Safe, economical automation using collaborative robots can transform a manufacturing facility and overcome staffing shortfalls, but it takes additional investment and a systemized approach to automation in order to realize this change.
Read MoreRead Next
Registration Now Open for the Precision Machining Technology Show (PMTS) 2025
The precision machining industry’s premier event returns to Cleveland, OH, April 1-3.
Read More5 Rules of Thumb for Buying CNC Machine Tools
Use these tips to carefully plan your machine tool purchases and to avoid regretting your decision later.
Read MoreBuilding Out a Foundation for Student Machinists
Autodesk and Haas have teamed up to produce an introductory course for students that covers the basics of CAD, CAM and CNC while providing them with a portfolio part.
Read More







.png;maxWidth=150)
























.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)













