Getting in Touch with Optimal EDM Results
Makino’s Hyper i control for wire EDM uses touchscreen navigation in its user interface, which helps a basic user to match the productivity and capability of an experienced operator.
Share





For many years, it seemed that the best operators for EDM equipment had to have a certain “touch” or knack for this technology, which has sometimes had the reputation of being fussy or mysterious. Developers of EDM technology have worked hard to overcome this perception by making their offerings capable of optimal results without high levels of operator training or talent. Much of this attention has focused on the user interface for the EDM controller.
The most recent trend has been to adopt the latest interface technology used by smartphones and tablets. The Hyper i control from Makino (Mason, Ohio) is a case in point. It represents the new generation of controls for the company’s U series of wire EDMs. The interface uses the now-familiar touchscreen functions of tap, drag, swipe, pinch and spread using the fingers to navigate the software features. This form of gesture control is designed to give the interface a simple and natural feel that is comfortable and efficient. More important, the new control enables a basic user to do more with logical and easily utilized functions that equal the productivity and capability of an experienced operator, the company says.
This is especially significant for the wire EDM process because it is, in fact, one in which the variables can be subtle, the mechanics complex and the workpiece requirements quite stringent. All of these challenges are well-managed by the advanced features of the EDM controller, so the key to success is the ease of use and intuitive nature of its interface. The advantages can be classified into three critical areas: operation, maintenance and monitoring.
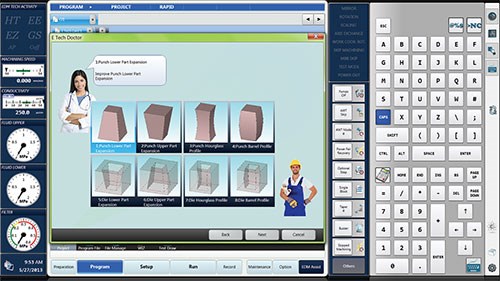
Operation covers the setup, programming and execution activities that are the operator’s duties. For each set of activities, the operator taps the intuitively understandable icon or menu choice to step through the sequence of actions. Touching with and then spreading two fingers enlarges the image or text provided for guidance. Swiping enables the user to “page through” onboard support materials quickly. During setup, for example, the operator may choose to access Makino’s E-Tech Doctor, a software feature that provides guidance for adjusting cutting conditions to create the intended result. This feature offers machine setting optimization related to corner accuracy, wall straightness and flatness of lead/entry point. By selecting the most appropriate setting, the cutting conditions are automatically determined by the machine for achieving these results.
Similar built-in intelligence streamlines maintenance routines. For example, an alert issued during lights-out operation overnight prompts the operator the next morning for a response. The operator brings up an image of the machine on the touchscreen of the control. A highly visible callout indicates that the energizer contact plates need attention. Tapping the callout immediately opens a new window that plays a video demonstration of the required maintenance procedure. Following the given instructions gets the task taken care of with timeliness and the least possible disruption.
For monitoring, the Hyper i provides a number of report screens that summarize data automatically collected to track consumables such as wire usage, de-ionizing resin supply and filter life. Other available reports analyze operations by showing detailed cycle-time information, actual versus estimated/quoted time, and comparisons of setup, cutting and idle time. This kind of intelligence helps ensure that unplanned stoppages due to emergency maintenance or consumable replenishment are minimized. Likewise, it helps identify and address opportunities to improve overall performance and productivity.
The control features a 24-inch, high-definition, flat touchscreen. The configuration of the display windows and settings can be customized for individual operators or shifts.
Related Content
Swiss-Type Control Uses CNC Data to Improve Efficiency
Advanced controls for Swiss-type CNC lathes uses machine data to prevent tool collisions, saving setup time and scrap costs.
Read MoreComputer Programming-Related Features of Custom Macro
Custom macro is an interpreter-based language, meaning that all CNC G code and custom macro commands are executed as the CNC comes across them.
Read MoreContinuous Improvement and New Functionality Are the Name of the Game
Mastercam 2025 incorporates big advancements and small — all based on customer feedback and the company’s commitment to keeping its signature product best in class.
Read MoreFive-Axis Machines Speed NASCAR Engine Production
Moving from an aging set of five-axis mills to more advanced machines enabled Hendrick Motorsports to dramatically improve its engine production.
Read MoreRead Next
Building Out a Foundation for Student Machinists
Autodesk and Haas have teamed up to produce an introductory course for students that covers the basics of CAD, CAM and CNC while providing them with a portfolio part.
Read More5 Rules of Thumb for Buying CNC Machine Tools
Use these tips to carefully plan your machine tool purchases and to avoid regretting your decision later.
Read MoreSetting Up the Building Blocks for a Digital Factory
Woodward Inc. spent over a year developing an API to connect machines to its digital factory. Caron Engineering’s MiConnect has cut most of this process while also granting the shop greater access to machine information.
Read More























.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)







