Do's and Don'ts of Finishing Metal 3D-Printed Parts
Finishing 3D-printed parts requires different considerations than conventionally machined ones. One expert offers tips.
Share





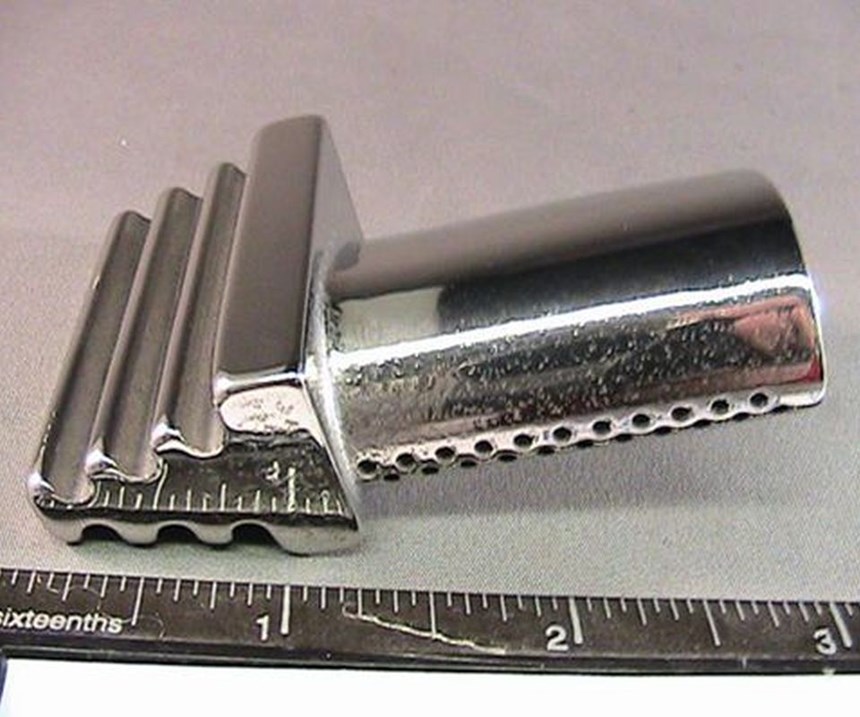
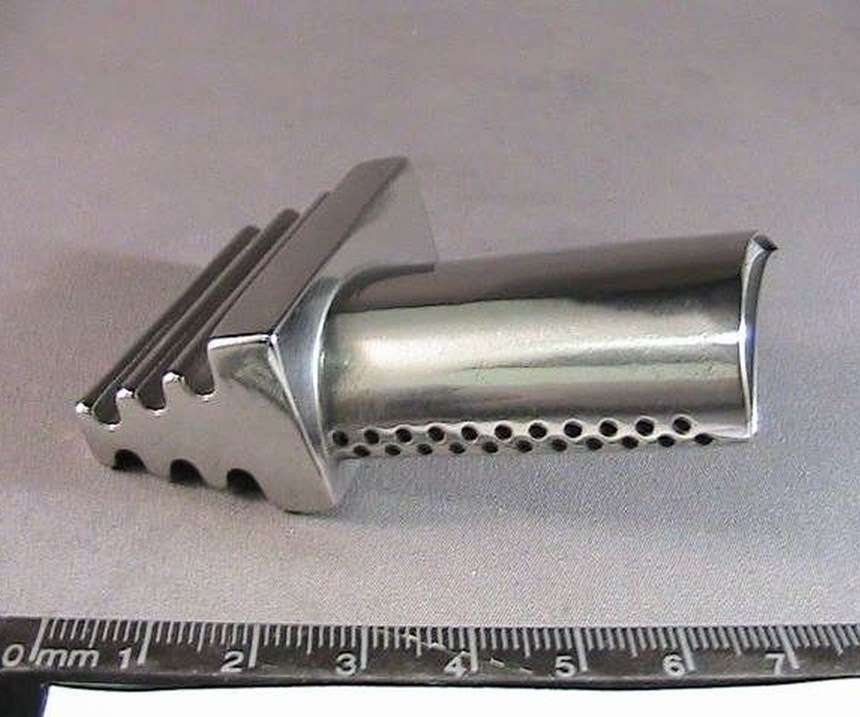
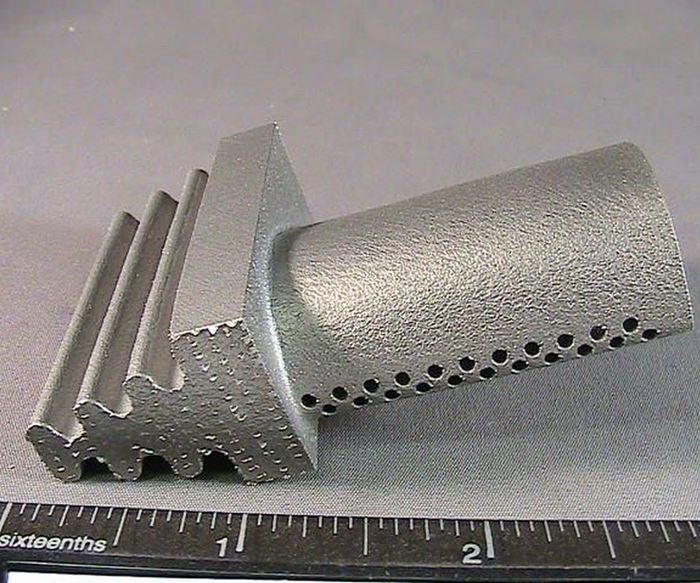
3D printing offers production advantages by allowing parts to be made with more complicated geometries, fewer components and limited assembly. But many 3D-printed parts will need some kind of finishing work, and this presents challenges when it comes to achieving quality surface finish.
Steven Alviti, president of Bel Air Finishing Supply of North Kingstown, Rhode Island, offers the following tips for improving the surface finish of 3D-printed metal parts:
Do understand there is no one technology that suits all 3D printing finishing applications. The surface of the printed part is directly affected by the type of printer, the printing technology and the material grain size. Finishing technologies must be mixed and matched with each individual part design based on material, printing techniques and part geometry. It is also important to note that multiple techniques can be used on the same part.
Don’t design a part with a conventional manufacturing thought process. Chances are that there will be dimensional challenges and/or surface finishing problems when a printed part is integrated into its functional assembly. Corner, angle and surface geometries will probably need to be built in an unconventional manner. Loss of material at a surface, other than a corner, can range between 0.001 to 0.005 inch.
Don’t design a part with the 3D hype mentality. The hype suggests that you can take a five-piece assembly and turn it into a one-shot build with your printer. But considering surface finish requirements and understanding that conventional finishing methods will not be applicable may make it necessary to break down and simplify the design. For example, a one-shot build could be divided into a two-part build with a single assembly. This may allow for standard finishing techniques to handle dimensional requirements and still have a more efficient process of production.
Do use a technique that Alviti refers to as the feedback loop. Using expert finishing recommendations, print a first article part of a design. Then evaluate the dimensional tolerance, surface finish and any lost geometry. Next, feed this information back to the build design. This may entail adding extra material and sharper corners, breaking the design into multiple parts, or even adding what is called a mask. This is a breakaway structure that can protect a particular part geometry from extra material removal.
Do define your surface finish requirements before you choose your 3D printing method, technology and part design. A part prints with many different surfaces finishes, depending on its orientation with relation to the build plate, the position in the box and its own geometry. So, for the best surface finish, take into account the printing method and critical surfaces in orienting the part. Keep in mind that the speed of a build and the resulting surface finish are at opposite ends of the spectrum. For example, the lower the starting as-printed Ra, the more likely and faster you will achieve the required surface specification.
Do understand postprocessing finishing techniques. The finishing process should include an appropriate cleaning process as well as wet grinding for the gross surface smoothing operation. It is important to note, however, that wet grinding and other mechanical surface finishing methods require material removal; these effects must be fed back into the build geometry and orientation to compensate for the loss.
Do take the time to understand and experiment with whatever finishing methods you have available. Have some specifically designed shapes built in several machine technologies and then have the surfaces finished by conventional methods to analyze the results and limitations before you purchase or before you design a part.
For more detail and additional finishing examples, read this article from Additive Manufacturing, sister publication to Modern Machine Shop.
Related Content
The Benefits of Vertically Integrating Metal 3D Printing and Machining
Having 3D printing and machining within one organization enables Addman’s engineers to collaborate and consolidate so it can quickly make successful metal 3D printed parts.
Read More6 Trends in Additive Manufacturing Technology
IMTS 2024 features a larger Additive Manufacturing Pavilion than ever before, with veteran suppliers alongside startups and newcomers at the front of the West Building. As you browse these exhibitors, as well as booths found elsewhere at the show, keep an eye out for these trends in AM.
Read MoreDigital Transparency in Machining Key to Multi-Site Additive Manufacturing
Cumberland Additive’s CNC programmer in Pennsylvania spends most of his time writing programs for machine tools in Texas.
Read MoreDigitalization and Done-In-One Reign Supreme at BIEMH 2024
European manufacturers may have a different balance of markets than their U.S. counterparts, but the practical challenges they must overcome are often similar — as are the solutions.
Read MoreRead Next
Setting Up the Building Blocks for a Digital Factory
Woodward Inc. spent over a year developing an API to connect machines to its digital factory. Caron Engineering’s MiConnect has cut most of this process while also granting the shop greater access to machine information.
Read MoreBuilding Out a Foundation for Student Machinists
Autodesk and Haas have teamed up to produce an introductory course for students that covers the basics of CAD, CAM and CNC while providing them with a portfolio part.
Read More5 Rules of Thumb for Buying CNC Machine Tools
Use these tips to carefully plan your machine tool purchases and to avoid regretting your decision later.
Read More
























.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)







