More Accurate Taper Cutting with Wire EDM
Cutting tall, steeply tapered surfaces with wire EDM often creates an overburn situation if the slope of the wire path changes from the top to the bottom of the cut. A feature called Volumetric Taper Compensation with four-axis overburn control compensates for this effect on FANUC wire EDM models from Methods Machine Tools Inc.
Share





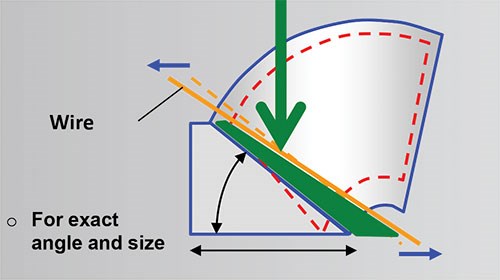
Cutting tall, steeply tapered surfaces with wire EDM is a challenging operation, especially if the wire must travel a greater distance at opposite ends of the taper in four-axis moves. One example is a taper cut that follows a curve such as to produce a cone-shaped geometry. Another example is cutting a slope in which the angle of the slope varies because one end of the slope is wider than the other. One of the chief difficulties in these situations arises because the wire traverse speed relative to the workpiece surface becomes slower as the wire approaches the progressively tighter arc of the cone shape or the narrower width of the slope.
This change in relative wire traverse speed creates conditions for an overburn where the part shape is tighter or narrower. The slower relative speed causes the energized wire to remove proportionately more material by producing an unwanted concentration of spark action in this portion of the workpiece. In addition to degrading geometric accuracy, this concentration of sparks may also cause the wire to break. A feature to compensate for this effect has been introduced on FANUC wire EDM models from Methods Machine Tools Inc. (Sudbury, Massachusetts).
Called Volumetric Taper Compensation with four-axis overburn control or TPCMP (for toolpath compensation), this feature is available first on the FANUC RoboCut a-CiA series of wire machines equipped with FANUC series 31i-WB controls. It enables the programmer to apply a single numerical value that determines the appropriate change in wire angle at both the upper and lower positions of the wire guides. Essentially, this change in wire angle adjusts the position of the wire in relation to the workpiece surface so that cutting conditions are the same along the full length of the wire in the cut. This adjustment moves the wire slightly farther away from the surface at one end of the cut and slightly closer to the surface at the opposite end. The result is enhanced cutting accuracy and lower risk of wire breakage. According to developers, taper cutting accuracy improves from 0.00122 inch to 0.0008 inch.
The appropriate compensation values are based on a simple test cut that the customer must do using his or her material and cutting parameters. The cutting results are measured and the resulting data is plugged into a formula that then provides the TPCMP value for each cutting pass. Although this compensation feature is most valuable in extreme taper cutting operations, it can be applied to any wire tool path involving independent U- or V-axis motions for improved accuracy.
The FANUC RoboCut a-CiA series from Methods Machine Tools includes a C400 model with X, Y and Z travels of 14.6, 10.6 and 10.2 inches, respectively, and U and V travels of ±2.362 inches. A C600 model is available in two versions, one with X, Y and Z travels of 23.6, 15.7 and 12.2 inches respectively, and U and V travels of ±3.937 inches; and another with a Z travel extended to 16.2 inches.
The builder recommends this series for machining a range of materials including cobalt-chrome, high-nickel alloys and titanium often found in applications such as aerospace, medical and military. For efficient graphite cutting, a new Pulse Mode has been designed specifically for machining very thin ribs in a single pass, resulting in time savings and consistency when machining electrodes. For applications in nickel alloys, stainless steel and titanium, an anti-recast power supply produces surfaces with no defects detectable at 1,000 magnification, the developers say.
Related Content
Lean Approach to Automated Machine Tending Delivers Quicker Paths to Success
Almost any shop can automate at least some of its production, even in low-volume, high-mix applications. The key to getting started is finding the simplest solutions that fit your requirements. It helps to work with an automation partner that understands your needs.
Read MoreThe Future of High Feed Milling in Modern Manufacturing
Achieve higher metal removal rates and enhanced predictability with ISCAR’s advanced high-feed milling tools — optimized for today’s competitive global market.
Read MoreBallbar Testing Benefits Low-Volume Manufacturing
Thanks to ballbar testing with a Renishaw QC20-W, the Autodesk Technology Centers now have more confidence in their machine tools.
Read MoreHow to Mitigate Chatter to Boost Machining Rates
There are usually better solutions to chatter than just reducing the feed rate. Through vibration analysis, the chatter problem can be solved, enabling much higher metal removal rates, better quality and longer tool life.
Read MoreRead Next
Registration Now Open for the Precision Machining Technology Show (PMTS) 2025
The precision machining industry’s premier event returns to Cleveland, OH, April 1-3.
Read More5 Rules of Thumb for Buying CNC Machine Tools
Use these tips to carefully plan your machine tool purchases and to avoid regretting your decision later.
Read MoreSetting Up the Building Blocks for a Digital Factory
Woodward Inc. spent over a year developing an API to connect machines to its digital factory. Caron Engineering’s MiConnect has cut most of this process while also granting the shop greater access to machine information.
Read More




















.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)









