Vickers Engineering is full of robots. Many are both large and powerful, and most move blindingly fast, fulfilling singular roles with such singular purpose that entering their protective cages requires rigid adherence to stringent safety protocols. The advantages of the latest collaborative arms aside, high part volumes, a breakneck production pace and an environment saturated with wear-inducing coolant and oil residue make traditional machine-tending automation the only choice for this Tier 1 automotive manufacturer.
However, Vickers’ success is due largely to making good on the idea that industrial robots can be more versatile than many believe. Perhaps the best proof of this is a relatively large structure near the center of the shop floor and emblazoned with a conspicuous logo: a red rabbit.
Within, a robot hangs suspended, manipulating work around the tombstone fixtures of three HMCs as well as an auxiliary pressing station. The six-axis industrial arm moves freely about a workzone clear of electrical cabinets, controllers and other necessary components, all of which are mounted on the roof. Ethernet cables, sensor connections and other necessary wiring snakes out-of-the-way and out-of-sight through the frame’s hollow steel weldments. If the work dries up, the entire system can be moved to a new location and adapted to a new job with modular components such as reconfigurable part drawers and infeed/outfeed systems.
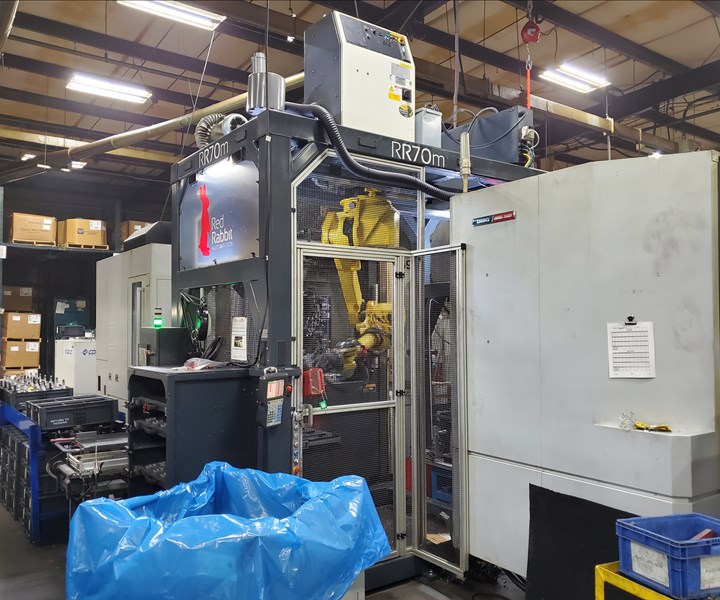

Robert Kracker, director of automation, emphasizes that putting robots in frames does not necessarily make redeploying robots easy. However, it does make it easier than starting from scratch. Making industrial robots easier to deploy and redeploy helps reduce the overall cost of automation and stretch significant, upfront design and implementation costs as far as possible. The next time Vickers gets a new contract, it will almost certainly take the same approach, he says.
In fact, he and his team already have assembled five different configurations of what they call the Redeployable Robot, just not on their own shop floor. Helping other, similar businesses apply similar systems is the work of a new side venture, Red Rabbit. In this way, Vickers stretches investments in in-house automation expertise in the same way that it stretches investments in the automation itself.
CNC Machining in Focus
In the lingo of automation integration, “red rabbit” refers to a deliberately faulty part used to test a system. Those that don’t understand the term are likely to be ideal customers for the new business, Mr. Kracker says (assuming their work justifies industrial robots).
These ideal customers also tend to look a lot like Vickers, or at least what Vickers might look like if the company had not focused so heavily and so early on automation. People here know the term “red rabbit” because the in-house engineering team has been regularly conducting these tests since before the company installed its first robot more than 15 years ago. Helping others complete the same journey in a shorter timeframe provided an opportunity to benefit from automation integration expertise when there are no new or ongoing projects, Mr. Kracker says.
“We’re an automation integrator with machining in our DNA.” – Robert Kracker
For now, Vickers’ and Red Rabbit’s engineering teams are one and the same, although some devote themselves more to one entity than the other. However, the side venture has grown to the point that it now operates from its own facility in Niles, Michigan, just a few miles from Vickers’ 120,000-square-foot plant in New Troy. Since the formal launch of the integration service in late 2017, Mr, Kracker says that work on outside applications has bolstered his confidence that the company offers a truly differentiated service. “We’re an automation integrator with machining in our DNA,” he says.
Automation Gets a Head Start

Machineable top plates made the first system’s loading drawers relatively easy to reconfigure for a new job at Vickers. Other systems are available with vision-guided bin-picking.
Red Rabbit’s modular machine tending system is the embodiment of years of effort to streamline the initial phases of cell design and implementation, Mr. Kracker says. Although configurations and applications differ widely, all of the self-contained systems have cages, electrical boxes, control boxes and robots. Other available modules that can be mixed and matched as-needed include vision systems for bin-picking as well as stations for part blow-off, grinding, polishing, deburring or other secondary applications. Configuring these elements to work together in advance and incorporating them into a single, self-contained unit provides a head start on new projects. It also makes redeployment feasible, regardless of whether redeployment is desirable.

After machining, the cast brackets leave the system on an outbound conveyor.
The system on Vickers’ shop floor was the first to be constructed. It faced its first test with its first application, an oilfield-parts contract that fizzled in the midst of assembling the unit. Originally designed for a tubular component produced on three lathes, the system was reconfigured for a cast automotive bracket.
New geometry required new robot grippers, new fixtures at all stations and new programming. Nonetheless, the Redployable Robot, which fit neatly between the mills, proved its worth. “If we were doing it the old way, we would have had to get the robot into place; get the drawers into place; find a place for the electrical cabinet and robot controller cabinet and maybe even move the lathes around anyway; and the wire links would have been all messed up,” Mr. Kracker explains.
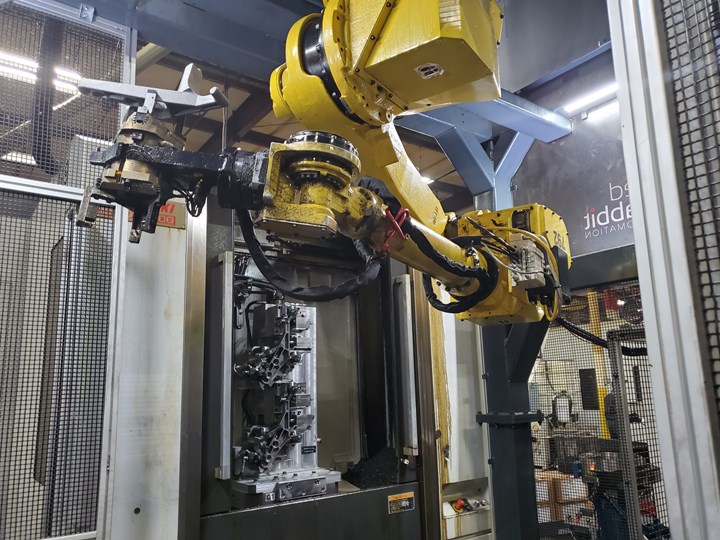

Hanging the robot upside down helps conserve floor space compared to traditional pedestal mounts. Two arms are available: the FANUC 710, which offers a payload of 70 kg, and the FANUC M20iB, which offers a payload of 25 kg.
(Semi-)Modular Machine Tending
Another retooling could potentially be accomplished in the same way, with far less waste than the process would otherwise entail. As an added benefit, the system is considered a single piece of equipment for depreciation purposes. Regardless, he emphasizes that redeploying the Redeployable Robot is not a job to be taken lightly. Best suited for multi-year part contracts, this is industrial automation by any definition, and challenges differ from application to application even within the same shop. “When it comes to implementing industrial automation, you can only standardize so much,” he says.
A project that was in the final phases of planning during Modern Machine Shop’s visit to Vickers provided a case in point. This four-machine cell will machine 21 different parts, some of which will enter from a lathe bar feeder and some of which will be robot-picked from a bin with guidance from a vision system. All parts undergo turning on the lathe, and most also pass through a VMC serviced by the same robot. The robot then places the partially machined workpieces on a regrip station for pickup by a second robot, which will manipulate them through one or both of the cell’s two grinding machines before depositing them on an outbound conveyor.
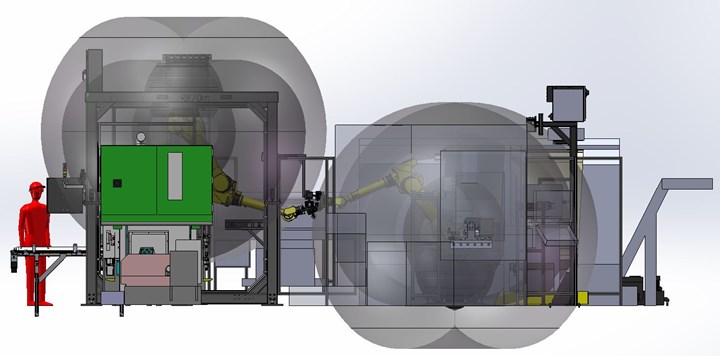
At first, the cell seemed ideal for two adjacent Redeployable Robots. However, closer examination revealed that reach limitations would make this approach impractical. One tradeoff for making the most of vertical space is limited reach, particularly at the lower end of the robot’s range. In this case, a robot suspended from a frame would not be able to reach the regrip station in the middle. In this case, simply arranging the equipment closer together to bring the regrip station within reach would make it impossible to clean the lathe’s coolant pan (and, as illustrated below, putting robots close to workstations can also require problem-solving). So, integrator and customer opted instead for a more traditional, pedestal-mounted robot on that side of the cell.
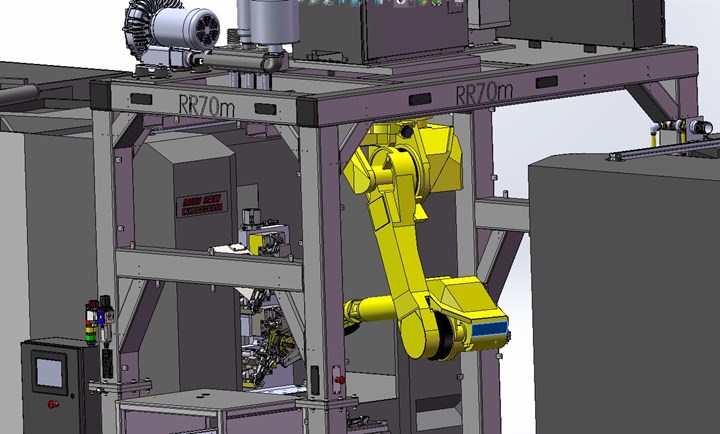
Inverting the robot’s third joint, as seen here, is a common solution for reach limitations that result from robots being placed close to machine tools.
Related Content
Increasing Productivity with Digitalization and AI
Job shops are implementing automation and digitalization into workflows to eliminate set up time and increase repeatability in production.
Read MoreLean Approach to Automated Machine Tending Delivers Quicker Paths to Success
Almost any shop can automate at least some of its production, even in low-volume, high-mix applications. The key to getting started is finding the simplest solutions that fit your requirements. It helps to work with an automation partner that understands your needs.
Read More3 Ways Artificial Intelligence Will Revolutionize Machine Shops
AI will become a tool to increase productivity in the same way that robotics has.
Read More4 Steps to a Cobot Culture: How Thyssenkrupp Bilstein Has Answered Staffing Shortages With Economical Automation
Safe, economical automation using collaborative robots can transform a manufacturing facility and overcome staffing shortfalls, but it takes additional investment and a systemized approach to automation in order to realize this change.
Read MoreRead Next
10 Ways to Think Differently about Robotic Automation
Take another look: A lot is happening in and around robotic automation. What robots might mean for machining and manufacturing is getting ready to change.
Read MoreVertical Machining Cells Challenge Horizontal Dominance
When part volumes are high, and success is measured in pennies and seconds, moving away from horizontal machines requires creative thinking about robotics, cutting tools, workholding and more.
Read MoreVideo: Automation Adds Jobs at Vickers Engineering
Rather than being a replacement for employees, this machined parts supplier says robotic automation has led to a doubling of the size of its staff.
Read More



















.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)