CAM Software Helps Shop Five-Axis Machine Aerospace Part
A five-axis machine and HyperMill CAM software from Open Mind Technologies gave a shop the ability to meet the tight tolerances required for the camera-mounting brackets on a NASA satellite mission.
Critical parts require tight tolerances, and these tolerances often cannot be met without powerful software. When Ramco Machine was contracted to machine camera-mount brackets out of Invar for a NASA satellite mission, it knew that it could meet the challenges and tight tolerances needed with the help of its five-axis machine and CAM software from Open Mind Technologies (Needham, Massachusetts).
Mike Jezowski is a vice president at Rowley, Massachusetts-based Ramco Machine, which was founded in the early 1980s by his parents. It began as a small machine shop that took on a range of jobs and has grown to include 30 employees. Mike and his brother Tim, also a vice president, handle day-to-day operations. The company specializes in complex milled and turned parts with stringent tolerances and fast turnaround times. Its range of projects include jobs for robotics companies and medical manufacturers.
In order to efficiently produce more complex jobs and “keep up with the times,” the shop decided to add five-axis machining capabilities two years ago by purchasing a DMU 65 FD MonoBlock mill-turn machining center from DMG MORI.
The next step for Ramco was to implement CAM software that could work with the capabilities of the new five-axis machine. “When you buy high-quality equipment, you need high-quality CAM software to program it,” Mr. Jezowski says. He had already researched CAM software for several years before purchasing the machine. The day the five-axis machine arrived, he ordered HyperMill software from Open Mind Technologies.
HyperMill is a modular CAM program for 2.5D, 3D, five-axis milling and mill turning. It includes applications and strategies for a range of machining operations. HyperMill gives users the ability to verify processes with machine and material-removal simulation before generating NC code. Its virtual machining also generates a simulation based on NC code.
Mr. Jezowski received in-house training from Open Mind, but he adds that reaching out to HyperMill’s support team has also taught him a lot. The support team can assist users in choosing machining cycles and strategies, and he says that working with different engineers has been a good way for him to learn the software. In fact, Ramco set up the software’s postprocessor with the help of Open Mind, a process that Mr. Jezowski says was fast and seamless. He also says the feature has been important to the company’s success, as some of the parts he has done are fairly complex.
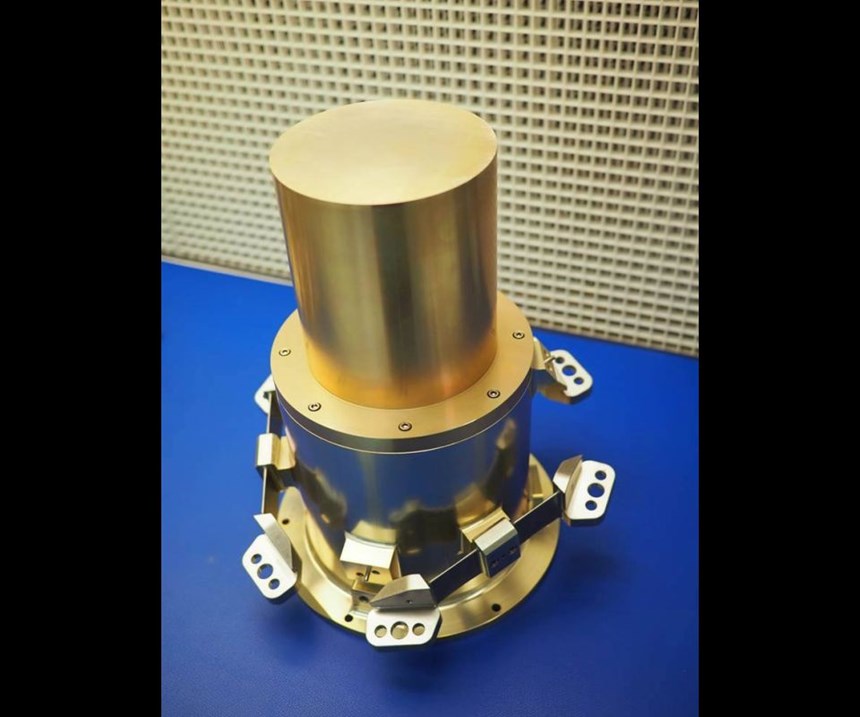
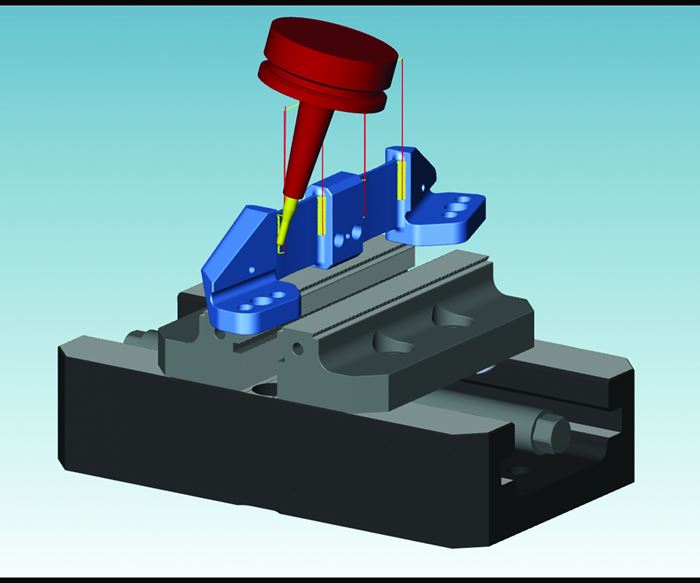
The shop has been able to take on new and different work thanks to the capabilities of its five-axis machine and software. For example, shortly after Ramco implemented HyperMill, it was contracted by MIT Lincoln Laboratory to make camera-mount brackets for NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) mission. The solar-powered satellite equipped with four ultra-sensitive cameras will be launched aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket to outer space. The camera system developed at the MIT Lincoln Laboratory will monitor the brightness of more than 200,000 stars during the two-year mission, and search for minute drops in brightness as planets move in front of each star. The job required a total of 32 brackets, 24 of one type of bracket and four each of two other types.
The mounting brackets needed to be made with Invar, a nickel-iron alloy with a low thermal-expansion coefficient that can withstand the rigors of launch and compensate for the extreme temperature swings of outer space. Mr. Jezowski says that its softness can pose problems, especially when drilling holes like the ones on the brackets.
Another challenge for Ramco was the tight acceptance tolerance for the parts. The brackets have two pads that had to be co-planar and perpendicular within 0.001 inch. The parts also have ribs that range from 0.050 inch ±0.001 inch in the middle to 0.080 inch ±0.001 inch at the end in their free state. The tight tolerances also meant that the brackets needed accurate surface finishes. “It couldn’t have any vibration or anything like that,” Mr. Jezowski says.
When planning how to machine the brackets, the shop took advantage of HyperMill’s support team to find a five-axis cycle to cut the ribs. “The ribs are extremely fussy and have small internal corners,” he says. The support team suggested a five-axis Z-level finishing cycle with a ballnose end mill.
The verification module was also key in helping Ramco meet the challenges of this job. “It’ll check the model against everything,” he adds. “I don’t have to run it through any additional third-party software.”
Ramco was able to achieve an accurate finish and tight tolerances to ship the camera-mounting brackets on time. Mr. Jezowski says the shop would not have been able to accomplish the required tolerances and finishes without five-axis capability.
He adds that the five-axis machine and software have not only enabled the shop to take on different kinds of work, it has also helped improve some of the shop’s other jobs. For instance, he says that three-axis machine work is often done better on the five-axis machine. Also, parts that previously had to be moved to other machines for finishing operations can now be completed on one machine.
Related Content
Why Go Five-Axis: Machine Types and Benefits
Even as the benefits of five-axis machining stack up year by year, the barrier for entry crumbles.
Read MoreChoosing a Five-Axis Machine Tool With Automation in Mind
While much focus is placed on the machinery that moves parts, the features most important for automating five-axis machining are arguably found in the machine tool itself.
Read MoreBallbar Testing Benefits Low-Volume Manufacturing
Thanks to ballbar testing with a Renishaw QC20-W, the Autodesk Technology Centers now have more confidence in their machine tools.
Read MoreHeavy Engineering: The Complex Logistics of Moving Large Machine Tools
One of our fascinations with large-format machine tools has little to do with their capabilities, but everything to do with the logistics involved with getting them up and running. Here’s how one of the world’s oldest builders of giant machine tools tackles the challenge.
Read MoreRead Next
Obscure CNC Features That Can Help (or Hurt) You
You cannot begin to take advantage of an available feature if you do not know it exists. Conversely, you will not know how to avoid CNC features that may be detrimental to your process.
Read MoreThe Cut Scene: The Finer Details of Large-Format Machining
Small details and features can have an outsized impact on large parts, such as Barbco’s collapsible utility drill head.
Read More3 Mistakes That Cause CNC Programs to Fail
Despite enhancements to manufacturing technology, there are still issues today that can cause programs to fail. These failures can cause lost time, scrapped parts, damaged machines and even injured operators.
Read More




















.png;maxWidth=300;quality=90)









