The Promise of Waterjet Technology for Micromachining
The potential benefits of using waterjet technology to produce parts or part features smaller than 300 microns are compelling. Developers and researchers are getting close to breaking the barriers that stand in the way of micromachining in the 150- to 200-micron range and below.
Share
Creating a high-pressure stream of water bearing an abrasive grit has proven to be a very effective way of cutting metal, plastic, glass and many other materials. Waterjet machining is the common name for this process. With multi-axis stream control and other accessories in place, it is possible to cut 3D forms to a level of precision and accuracy that matches or exceeds other metal removal processes. However, in many cases, waterjet machining has additional benefits.
It may cut faster. It leaves no heat-affected zone. Workpiece materials do not need to be electrically conductive or non-reflective. Change-over time can be minimal because only the new part program has to be downloaded to the CNC.
Highly flexible and capable, waterjet continues to find new applications in precision manufacturing, especially in cases where cost-effectiveness and fast turnaround are critical. One area that has attracted considerable attention is applying waterjet to the production of parts in the “micro” range, that is, parts or part features smaller than 300 microns. R&D efforts are currently focused on making waterjet practical in the 150- to 200-micron range.
Dr. Peter Liu, senior scientist at Omax Corporation (Kent, Washington) is deeply involved in exploring the frontier of micro-abrasive waterjet technology, as it is called. In fact, his on-going efforts to further the development of this process are supported by a grant from the National Science Foundation Small Business Innovation Research Program (NSF SBIR Phase II grant 1058278) as well as Omax’s own R&D funds.
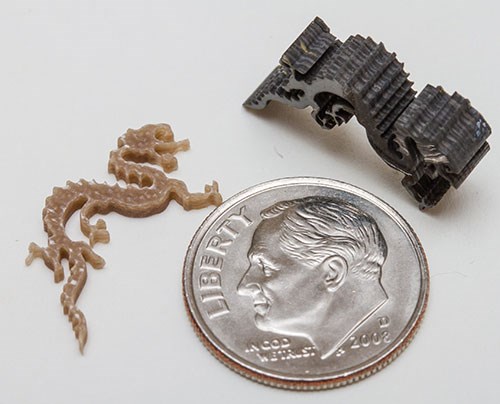
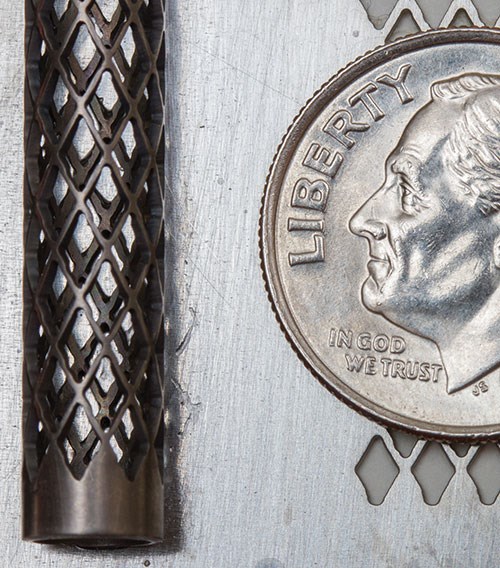
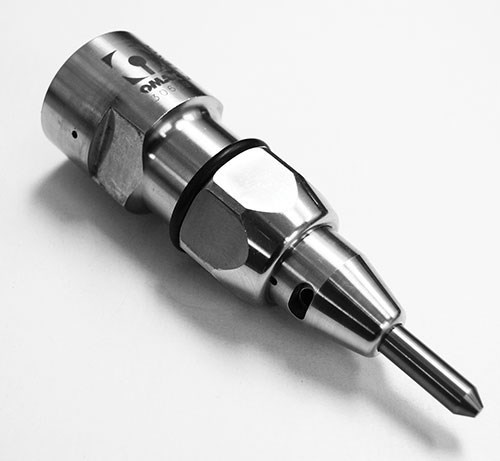
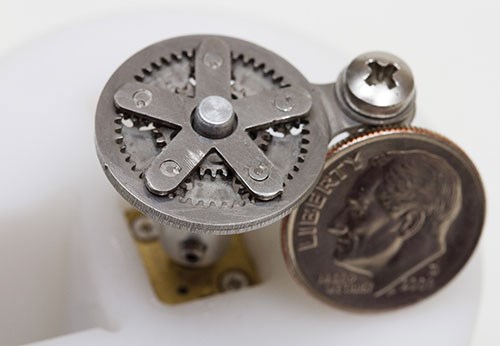
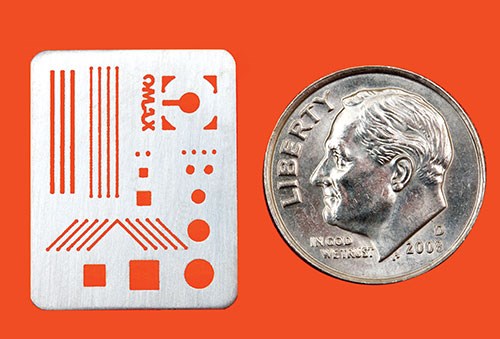
As the gallery of sample parts shown in this article demonstrates, waterjet is already capable of remarkable success in producing small parts and features. To push waterjet technology to greater capability in the micromachining arena, Dr. Liu says that research efforts must overcome barriers in three critical areas.
One is a practical method to produce a nozzle orifice 100 microns or smaller in diameter. Current methods cannot produce a hole this small with adequate roundness or straightness, he says. Wear resistance of the nozzle material is also a problem.
Likewise, a mixing tube, the component of the stream delivery system in which water and the abrasive particles meet to form a slurry, must be designed to function effectively on a highly miniaturized scale. Downsizing current designs is limited by the existing science in fluid dynamics. For example, researchers are studying surface tension, capillary action, supersonics and the Venturi effect for insights that may lead to breakthroughs.
For waterjet micromachining, the size of abrasive particles must be reduced proportionately. Thus, a third challenge is developing methods to feed abrasive particles in orders of magnitude finer than is currently feasible. Because the behavior of ultra-fine particles is not fully understood (particularly in the area of gravity feeding), achieving constant flow rates for consistent and predictable cutting quality has been elusive.
Despite these challenges, Dr. Liu feels he has made considerable progress in the development of micro-waterjet machining technology. He expects this technology to become a viable process with competitive advantages for micro-machining applications in the targeted micro-range. He predicts a two- to four-year time frame for this achievement.
In the meantime, manufacturers must look closely at waterjet and think creatively
about opportunities it presents for making extremely small parts to high precision.
Related Content
Hamar Laser Instruments Surface Plate Calibration System Increases Repeatability
IMTS 2024: Hamar Laser Instruments introduces the L-703SP surface plate calibration system, intended to reduce time for surface plate calibration by 30 to 60%.
Read More3 Lessons Job Shops Can Learn From Laser Cutters
This laser-cutting “job shop” designs its processes to make high-mix, low volume work profitable.
Read MoreFlow Waterjet Cutting System Provides Fast Overall Cut Time
IMTS 2024: Flow’s Mach 200c five-axis cutting system features high-speed motors and drives for rapid speed and acceleration and deceleration.
Read MoreCeratizit Waterjet Nozzles Cut Difficult Materials
The HyproJet range features three standard waterjet nozzles designed to provide narrow hole tolerances, optimized cutting and radial run-out accuracy.
Read MoreRead Next
IMTS 2024: Trends & Takeaways From the Modern Machine Shop Editorial Team
The Modern Machine Shop editorial team highlights their takeaways from IMTS 2024 in a video recap.
Read MoreThe Future of High Feed Milling in Modern Manufacturing
Achieve higher metal removal rates and enhanced predictability with ISCAR’s advanced high-feed milling tools — optimized for today’s competitive global market.
Read MoreInside Machineosaurus: Unique Job Shop with Dinosaur-Named CNC Machines, Four-Day Workweek & High-Precision Machining
Take a tour of Machineosaurus, a Massachusetts machine shop where every CNC machine is named after a dinosaur!
Read More

























.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)







